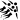Лусис, Янис Вольдемарович. Янис вольдемарович лусис
Лусис, Янис Вольдемарович — Википедия
Материал из Википедии — свободной энциклопедии
В Википедии есть статьи о других людях с фамилией Лусис.Я́нис Вольдема́рович Лу́сис (латыш. Jānis Lūsis; 19 мая 1939, Елгава, Латвия) — советский латвийский метатель копья, олимпийский чемпион (1968, Мехико), серебряный призёр Олимпийских игр (1972, Мюнхен), бронзовый призёр Олимпийских игр (1964, Токио). Чемпион Европы (1962, 1966, 1969, 1971). Чемпион СССР (1962—1966, 1968—1973, 1976). Рекордсмен мира (1968—1969, 1972—1973). Внесён в зал Славы ИААФ.
Биография
В 1961 году окончил Латвийский государственный институт физической культуры (латыш.)русск.. В 1965 году получил звание заслуженного мастера спорта. Карьеру профессионального спортсмена начал в 1957 году, закончил в 1976 году на Олимпийских играх в Монреале (8 место). Янис Лусис — единственный представитель Латвии, которому удалось завоевать олимпийские медали всех трёх проб. Личный рекорд — 93 м 80 см (1972).
| Советский копьеметатель Янис Лусис — бесспорно лучший легкоатлет прошедшего десятилетия (спортивная французская газета Equipe) |
Член КПСС с 1975 года.
Семья
Супруга Яниса Лусиса Эльвира Озолиня (род. 1939) — олимпийская чемпионка 1960 года в метании копья. Сын Яниса и Эльвиры Вольдемар Лусис (род. 1974) также стал копьеметателем и участвовал в Олимпийских играх 2000 и 2004 годов, не добившись особых успехов.
Видео по теме
Государственные награды
Литература
Ссылки
wikipedia.green
Лусис, Янис Вольдемарович
В Википедии есть статьи о других людях с фамилией Лусис .Я́нис Вольдема́рович Лу́сис ( латыш. Jānis Lūsis ; 19 мая 1939 , Елгава , Латвия ) — советский латвийский метатель копья , олимпийский чемпион (1968, Мехико ), серебряный призёр Олимпийских игр (1972, Мюнхен ), бронзовый призёр Олимпийских игр (1964, Токио ). Чемпион Европы (1962, 1966, 1969, 1971). Чемпион СССР (1962—1966, 1968—1973, 1976). Рекордсмен мира (1968—1969, 1972—1973). Внесён в зал Славы ИААФ .
Биография
В 1961 году окончил Латвийский государственный институт физической культуры (латыш.) русск. . В 1965 году получил звание заслуженного мастера спорта. Карьеру профессионального спортсмена начал в 1957 году, закончил в 1976 году на Олимпийских играх в Монреале (8 место). Янис Лусис — единственный представитель Латвии, которому удалось завоевать олимпийские медали всех трёх проб. Личный рекорд — 93 м 80 см (1972).
| Советский копьеметатель Янис Лусис — бесспорно лучший легкоатлет прошедшего десятилетия (спортивная французская газета Equipe ) |
Член КПСС с 1975 года.
Семья
Супруга Яниса Лусиса Эльвира Озолиня (род. 1939 ) — олимпийская чемпионка 1960 года в метании копья. Сын Яниса и Эльвиры Вольдемар Лусис (род. 1974 ) также стал копьеметателем и участвовал в Олимпийских играх 2000 и 2004 годов, не добившись особых успехов.
Государственные награды
Литература
Ссылки
www.cruer.com
| Латвия | ||||||||||||||||
| 295331 | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Янис Вольдемарович Лусис на Викискладе | ||||||||||||||||
| Советский копьеметатель Янис Лусис — бесспорно лучший легкоатлет прошедшего десятилетия (спортивная французская газета Equipe) |
Семья
Супруга Яниса Лусиса Эльвира Озолиня (род. 1939) — олимпийская чемпионка 1960 года в метании копья. Сын Яниса и Эльвиры Вольдемар Лусис (род. 1974) также стал копьеметателем и участвовал в Олимпийских играх 2000 и 2004 годов, не добившись особых успехов.
Государственные награды
- орден Трудового Красного Знамени
- орден «Знак Почёта»
- орден Трёх звезд
- Заслуженный мастер спорта СССР
Ссылки
- Фото Яниса Лусиса
- Биография Яниса Лусиса
- Янис Лусис — олимпийская статистика на сайте Sports-Reference.com (англ.)
| |||||
| ||||||
Лусис, Янис Вольдемарович Информация о

Лусис, Янис Вольдемарович Комментарии
Лусис, Янис ВольдемаровичЛусис, Янис Вольдемарович Лусис, Янис Вольдемарович Просмотр темы.
Лусис, Янис Вольдемарович что, Лусис, Янис Вольдемарович кто, Лусис, Янис Вольдемарович объяснение
There are excerpts from wikipedia on this article and video
www.turkaramamotoru.com
Лусис, Янис Вольдемарович - Howling Pixel
Я́нис Вольдема́рович Лу́сис (латыш. Jānis Lūsis; 19 мая 1939, Елгава, Латвия) — советский латвийский метатель копья, олимпийский чемпион (1968, Мехико), серебряный призёр Олимпийских игр (1972, Мюнхен), бронзовый призёр Олимпийских игр (1964, Токио). Чемпион Европы (1962, 1966, 1969, 1971). Чемпион СССР (1962—1966, 1968—1973, 1976). Рекордсмен мира (1968—1969, 1972—1973). Внесён в зал Славы ИААФ.
Янис Вольдемарович Лусис | |
| 19 мая 1939 (79 лет) | |
| 180 см | |
| 90 кг | |
| 295331 | |
Биография
В 1961 году окончил Латвийский государственный институт физической культуры. В 1965 году получил звание заслуженного мастера спорта. Карьеру профессионального спортсмена начал в 1957 году, закончил в 1976 году на Олимпийских играх в Монреале (8 место). Янис Лусис — единственный представитель Латвии, которому удалось завоевать олимпийские медали всех трёх проб. Личный рекорд — 93 м 80 см (1972).
| Советский копьеметатель Янис Лусис — бесспорно лучший легкоатлет прошедшего десятилетия (спортивная французская газета Equipe) |
Член КПСС с 1975 года.
Семья
Супруга Яниса Лусиса Эльвира Озолиня (род. 1939) — олимпийская чемпионка 1960 года в метании копья. Сын Яниса и Эльвиры Вольдемар Лусис (род. 1974) также стал копьеметателем и участвовал в Олимпийских играх 2000 и 2004 годов, не добившись особых успехов.
Государственные награды
Литература
Ссылки
This page is based on a Wikipedia article written by authors (here). Text is available under the CC BY-SA 3.0 license; additional terms may apply. Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
howlingpixel.com
 Опубликовать Опубликовать | скачать Реферат на тему: План:
ВведениеJānis Lūsis Я́нис Вольдема́рович Лу́сис (латыш. Jānis Lūsis; 19 мая 1939, Елгава, Латвийская ССР, СССР) — советский латвийский метатель копья, олимпийский чемпион (1968, Мехико), серебряный призер Олимпийских игр (1972, Мюнхен), бронзовый призер Олимпийских игр (1964, Токио). Чемпион Европы (1962, 1966, 1969, 1971). Чемпион СССР (1962—1966, 1968—1973, 1976). Рекордсмен мира (1968—1969, 1972—1973). 1. БиографияВ 1961 году окончил Латвийский институт физической культуры. В 1965 году получил звание заслуженного мастера спорта. Карьеру профессионального спортсмена начал в 1957 году, закончил в 1976 году на Олимпийских играх в Монреале (8 место). Янис Лусис — единственный представитель Латвии, которому удалось завоевать олимпийские медали всех трёх проб. Личный рекорд — 93 м 80 см (1972). 1.1. СемьяСупруга Яниса Лусиса Эльвира Озолиня (род. 1939) — олимпийская чемпионка 1960 года в метании копья. Сын Яниса и Эльвиры Вольдемар Лусис (род. 1974) также стал копьеметателем и участвовал в Олимпийских играх 2000 и 2004 годов, не добившись особых успехов. 2. Государственные награды
Категории: Персоналии по алфавиту, Кавалеры ордена Трудового Красного Знамени, Кавалеры ордена Знак Почёта, Родившиеся 19 мая, Родившиеся в 1939 году, Заслуженные мастера спорта СССР, Олимпийские чемпионы от СССР, Чемпионы летних Олимпийских игр 1968 года, Легкоатлеты СССР, Олимпийские чемпионы по лёгкой атлетике, Родившиеся в Елгаве, Чемпионы Европы по лёгкой атлетике, Легкоатлеты на летних Олимпийских играх 1964 года, Серебряные призёры летних Олимпийских игр 1972 года, Легкоатлеты на летних Олимпийских играх 1968 года, Легкоатлеты на летних Олимпийских играх 1972 года, Легкоатлеты на летних Олимпийских играх 1976 года, Легкоатлеты Латвии, Бронзовые призёры летних Олимпийских игр 1964 года, Чемпионы СССР по лёгкой атлетике. Текст доступен по лицензии Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike. |
wreferat.baza-referat.ru
Лусис, Янис Вольдемарович - WikiVisually
1. Елгава – Jelgava is a city in central Latvia about 41 kilometres southwest of Riga with about 63,000 inhabitants. It is the largest town in the region of Zemgale, Jelgava was the capital of the united Duchy of Courland and Semigallia and the administrative center of the Courland Governorate. Jelgava is situated on a fertile plain rising only 3.5 metres above sea level on the right bank of the river Lielupe. At high water the plain and sometimes the town as well can be flooded and it is a railway center and is also host to Jelgava Air Base. Until 1917, the city was referred to as Mitau. The name Jelgava is believed to be derived from the Livonian word jālgab, an alternate explanation is that Mitau came from Mitte in der Aue, German for the middle of the Aa, referring to the Lielupe River, formerly known as the Courland Aa. Jelgava before the Second World War had regular, broad streets lined with the mansions of the Baltic German nobility who resided at the capital of Courland. The old castle of the dukes of Courland, situated on an island in the river, was destroyed by Duke Biren, the palace contains the sarcophagi of almost all of the Curonian dukes, except the last one. The future Louis XVIII sojourned in the palace between 1798 and 1800 and it now functions as the LLU, Latvijas Lauksaimniecības Universitāte, or Latvian University of Agriculture. Other landmarks include the Baroque church of St. Anne, the tower of the destroyed Trinity church, the Livonian settlement Jelgava began developing between the rivers Lielupe and Driksa during the 10th century. Led by the Grand Master Konrad von Mander, the crusading Livonian Order constructed the castle in Mitau on an island fortification in 1265–1266. Using Mitau as a fortress, the German knights subdued the surrounding Livonians and Semigallians by 1290. The town rose in importance as a fixture against the Lithuanians to the south. As a result of the fall of the Livonian Order in the Livonian War, Jelgava received city rights in 1573, and became the capital of the united duchies of Courland and Semigallia in 1578. When the Duchy of Courland split in 1596, Jelgava became the residence of Duke Friedrich Kettler of Semigallia, the city again became the capital of the united duchies in 1617. Because the duchy became a vassal of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Jelgava was also referred to by the Polish name Mitawa, the Commonwealths repeated wars with Sweden subjected Jelgava to several sieges. Despite the wars, the city grew as a center for trade, the duchess from 1711 to 1730 was Anna Ivanovna, later Empress Anna I of Russia. The penultimate duke of Courland, Ernst Johann von Biron, expanded the cultural aspects of Jelgava and he constructed the ducal palace and opened the first public library in the city
2. Латвия – Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe, one of the three Baltic states. It is bordered by Estonia to the north, Lithuania to the south, Russia to the east, Latvia has 1,957,200 inhabitants and a territory of 64,589 km2. The country has a seasonal climate. Latvia is a parliamentary republic established in 1918. The capital city is Riga, the European Capital of Culture 2014, Latvia is a unitary state, divided into 119 administrative divisions, of which 110 are municipalities and 9 are cities. Latvians and Livs are the people of Latvia. Latvian and Lithuanian are the two surviving Baltic languages. Despite foreign rule from the 13th to 20th centuries, the Latvian nation maintained its identity throughout the generations via the language, Latvia and Estonia share a long common history. Until World War II, Latvia also had significant minorities of ethnic Germans, Latvia is historically predominantly Protestant Lutheran, except for the Latgale region in the southeast, which has historically been predominantly Roman Catholic. The Russian population has brought a significant portion of Eastern Orthodox Christians. The Republic of Latvia was founded on 18 November 1918, however, its de facto independence was interrupted at the outset of World War II. The peaceful Singing Revolution, starting in 1987, called for Baltic emancipation of Soviet rule and it ended with the Declaration on the Restoration of Independence of the Republic of Latvia on 4 May 1990, and restoring de facto independence on 21 August 1991. Latvia is a democratic and developed country and member of the European Union, NATO, the Council of Europe, the United Nations, CBSS, the IMF, NB8, NIB, OECD, OSCE, and WTO. For 2014, Latvia was listed 46th on the Human Development Index and it used the Latvian lats as its currency until it was replaced by the euro on 1 January 2014. The name Latvija is derived from the name of the ancient Latgalians, one of four Indo-European Baltic tribes, henry of Latvia coined the Latinisations of the countrys name, Lettigallia and Lethia, both derived from the Latgalians. The terms inspired the variations on the name in Romance languages from Letonia. Around 3000 BC, the ancestors of the Latvian people settled on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea. The Balts established trade routes to Rome and Byzantium, trading local amber for precious metals, by 900 AD, four distinct Baltic tribes inhabited Latvia, Curonians, Latgalians, Selonians, Semigallians, as well as the Livonians speaking a Finnic language
3. Международная ассоциация легкоатлетических федераций – The International Association of Athletics Federations is the international governing body for the sport of athletics. It was founded on 17 July 1912 as the International Amateur Athletic Federation by representatives from 17 national athletics federations at the organizations first congress in Stockholm, since October 1993, it has been headquartered in Monaco. Beginning in 1982, the IAAF passed several amendments to its rules to allow athletes to receive compensation for participating in international competitions. However, the organization retained the word amateur in its name until its 2001 congress, the IAAFs president is Sebastian Coe of the United Kingdom. He was elected at the 2015 congress before the 2015 World Championships in Athletics in Beijing, the process to found the IAAF was started at a meeting in Stockholm, Sweden on July 17,1912 soon after the completion of the 1912 Summer Olympics in that city. The congress that started on August 20,1913 in Berlin is when the foundation of the IAAF was formally completed, in 2015, a whistleblower leaked IAAFs blood test records from major competitions. After reviewing the results, Robin Parisotto, a scientist and leading anti-doping expert, said, so many athletes appear to have doped with impunity, and it is damning that the IAAF appears to have idly sat by and let this happen. Craig Reedie, president of the World Anti-Doping Agency, said his organisation was very disturbed by these new allegations, which will, once again, shake the foundation of clean athletes worldwide, and that its independent commission will investigate the claims. On 1 November 2015, former IAAF president Lamine Diack was arrested in France and is under investigation on suspicion of corruption, Diack allegedly accepted $1.2 million from the Russian athletics federation to cover up the positive doping tests of at least six Russian athletes in 2011. The report continued that the IAAF allowed the conduct to occur and must accept its responsibility and that corruption was embedded in the organization. In January 2016, as a result of the scandal and WADAs report. The BBC reported that as a result the IAAF would lose $33 million worth of revenue, the 11-year sponsorship deal with Adidas was due to run until 2019. World-record holding sprinter, Michael Johnson, described the scandal as more serious than that faced by FIFA, in February,2016, Nestle announced that it was ending its IAAF sponsorship. In June 2016, following a meeting of the IAAFs ruling council, in Ferbuary 2017, All-Russia Athletic Federation disqualified by decision of the IAAF Council for 8 years for the creation of a doping system. Since the establishment of the IAAF, it has had six presidents, The IAAF has a total of 215 member federations divided into 6 area associations
4. Летние Олимпийские игры – The Summer Olympic Games or the Games of the Olympiad, first held in 1896, is an international multi-sport event that is hosted by a different city every four years. The most recent Olympics were held in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, the International Olympic Committee organizes the games and oversees the host citys preparations. In each Olympic event, gold medals are awarded for first place, silver medals are awarded for second place, and bronze medals are awarded for third, the Winter Olympic Games were created due to the success of the Summer Olympics. The Olympics have increased in scope from a 42-event competition with fewer than 250 male competitors from 14 nations in 1896 to 302 events with 10,768 competitors from 204 nations in 2012, eighteen countries have hosted the Summer Olympics. The United States has hosted four Summer Olympics, more than any other nation, four cities have hosted two Summer Olympics, Athens, Paris, Los Angeles, and Tokyo. Tokyo is the first city outside of the Western world to host the Summer Olympics multiple times, asia has hosted the Summer Olympics four times in Japan, South Korea, and China. The only Summer Olympics held in the Southern Hemisphere have been in Australia, the 2016 Games are the first Summer Olympics to be held in South America and the first to be held during the local winter season. Africa has yet to host a Summer Olympics, only five countries—Greece, Australia, France, Great Britain, and Switzerland—have been represented at every Summer Olympic Games. The only country to have won at least one medal at every Summer Olympic Games is Great Britain. The United States leads the medal table. Qualification rules for each of the Olympic sports are set by the International Sports Federations that governs that sports international competition, for individual sports, competitors typically qualify through attaining a certain place in a major international event or on the IFs ranking list. There is a rule that maximum three individual athletes may represent each nation per competition. Nations most often qualify teams for team sports through continental qualifying tournaments, each nation may be represented by no more than one team per competition a team is two people in some sports. The United States has hosted four Summer Olympic Games, more than any other nation, the United Kingdom hosted the 2012 Olympic Games, its third Summer Olympic Games, in its capital London, making London the first city to host the Summer Olympic Games three times. Australia, France, Germany, Greece, and Japan have all hosted the Summer Olympic Games twice. Other countries that have hosted the Summer Olympics are Belgium, Brazil, China, Canada, Finland, Italy, Mexico, Netherlands, South Korea, Spain, the Soviet Union, asia has hosted the Summer Olympics three times and will host again in 2020. In 2016, Rio de Janeiro hosted the first Summer Olympics in South America, three cities have hosted two Summer Olympic Games, Los Angeles, Paris, and Athens. Stockholm has hosted events at two Summer Olympic Games, having hosted the games in 1912 and the events at the 1956 Summer Olympics—which they are usually listed as jointly hosting
5. Летние Олимпийские игры 1964 – The 1964 Summer Olympics, officially known as the Games of the XVIII Olympiad, was an international multi-sport event held in Tokyo, Japan, from October 10 to 24,1964. The 1964 Summer Games were the first Olympics held in Asia, Tokyo was chosen as the host city during the 55th IOC Session in West Germany, on May 26,1959. These games were also the first to be telecast internationally without the need for tapes to be overseas, as they had been for the 1960 Olympics four years earlier. The games were telecast to the United States using Syncom 3, the first geostationary communication satellite and these were also the first Olympic Games to have color telecasts, albeit partially. Certain events like the sumo wrestling and judo matches, sports huge in Japan, were tried out using Toshibas new color transmission system, history surrounding the 1964 Olympics was chronicled in the 1965 documentary film Tokyo Olympiad, directed by Kon Ichikawa. The games were scheduled for mid-October to avoid the citys midsummer heat and humidity, the previous Olympics in Rome in 1960 started in late August and experienced hot weather. The following games in 1968 in Mexico City also began in October, the 1964 Olympics were also the last to use a traditional cinder track for the track events. A smooth synthetic all-weather track was used for the first time at the 1968 Olympics, the 2020 Summer Olympics will be held in Tokyo. Tokyo won the rights to the Games on May 26,1959, at the 55th IOC Session in Munich, West Germany, over bids from Detroit, Brussels and Vienna. Toronto was an early bidder again in 1964 after the attempt for 1960. Yūji Koseki composed the song of the opening ceremony. Yoshinori Sakai, who lit the Olympic Flame, was born in Hiroshima on August 6,1945, kumi-daiko was first exhibited to a world-wide audience at the Festival of Arts presentation. Judo and womens volleyball, both sports in Japan, were introduced to the Olympics. Japan won gold medals in three events, but Dutchman Anton Geesink won the Open category. The Japanese womens volleyball won the gold medal, with the final being broadcast live. The womens pentathlon was introduced to the athletics events, soviet gymnast Larisa Latynina won two gold medals, a silver medal and two bronze medals. She held the record for most Olympic medals at 18 which stood until broken by American swimmer Michael Phelps in 2012, czechoslovakian gymnast Věra Čáslavská wins 3 gold medals, including the individual all-around competition, crowning her the new queen over the reigning champion Larisa Latynina. Australian swimmer Dawn Fraser won the 100 m freestyle event for the time in a row
wikivisually.com
Лусис, Янис Вольдемарович - Википедия
Материал из Википедии — свободной энциклопедии
В Википедии есть статьи о других людях с фамилией Лусис.Я́нис Вольдема́рович Лу́сис (латыш. Jānis Lūsis; 19 мая 1939, Елгава, Латвия) — советский латвийский метатель копья, олимпийский чемпион (1968, Мехико), серебряный призёр Олимпийских игр (1972, Мюнхен), бронзовый призёр Олимпийских игр (1964, Токио). Чемпион Европы (1962, 1966, 1969, 1971). Чемпион СССР (1962—1966, 1968—1973, 1976). Рекордсмен мира (1968—1969, 1972—1973). Внесён в зал Славы ИААФ.
Биография[ | ]
В 1961 году окончил Латвийский государственный институт физической культуры (латыш.). В 1965 году получил звание заслуженного мастера спорта. Карьеру профессионального спортсмена начал в 1957 году, закончил в 1976 году на Олимпийских играх в Монреале (8 место). Янис Лусис — единственный представитель Латвии, которому удалось завоевать олимпийские медали всех трёх проб. Личный рекорд — 93 м 80 см (1972).
| Советский копьеметатель Янис Лусис — бесспорно лучший легкоатлет прошедшего десятилетия (спортивная французская газета Equipe) |
Семья[ | ]
Супруга Яниса Лусиса Эльвира Озолиня (род. 1939) — олимпийская чемпионка 1960 года в метании копья. Сын Яниса и Эльвиры Вольдемар Лусис (род. 1974) также стал копьеметателем и участвовал в Олимпийских играх 2000 и 2004 годов, не добившись особых успехов.
Государственные награды[ | ]
Ссылки[ | ]
encyclopaedia.bid