Зимние Олимпийские игры 1998. Зимние олимпийские игры 1998
Зимние Олимпийские игры 1998 — Википедия
XVIII зимние Олимпийские игры проводились в японском городе Нагано в период с 7 февраля по 22 февраля 1998 года. Другими кандидатами на проведение игр были итальянская Аоста, шведский Эстерсунд, испанская Хака, Солт-Лейк-Сити (США). По общему мнению, сложная победа (46:42 в последнем туре голосования) над Солт-Лейк-Сити досталась Нагано за счет «фактора Атланты» — то есть благодаря тому, что летние ОИ 1996 уже были отданы США.
Нагано стал самым близким к экватору городом, принимавшим Зимние игры, и остаётся им до сих пор.
Итоги Олимпийских игр[править]
| Горные лыжи (Яманоути/Якэбитай/Хаукба) | Скоростной спуск, мужчины | 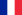 Жан-Люк Кретье Жан-Люк Кретье | 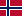 Лассе Чьюс Лассе Чьюс |  Ханнес Тринкль Ханнес Тринкль |
| Супергигант, мужчины |  Херманн Майер Херманн Майер | 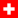 Дидье Кюш, Дидье Кюш,  Ханс Кнаусс Ханс Кнаусс | ||
| Слалом-гигант, мужчины |  Херманн Майер Херманн Майер |  Штефан Эберхартер Штефан Эберхартер |  Михаэль фон Грюниген Михаэль фон Грюниген | |
| Слалом, мужчины |  Ханс Петтер Бурос Ханс Петтер Бурос |  Уле Кристиан Фурусет Уле Кристиан Фурусет |  Томас Сикора Томас Сикора | |
| Комбинация, мужчины |  Марио Райтер Марио Райтер |  Лассе Чьюс Лассе Чьюс |  Кристиан Майер Кристиан Майер | |
| Скоростной спуск, женщины |  Катя Зайцингер Катя Зайцингер | 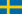 Пернилла Виберг Пернилла Виберг |  Флоранс Маснада Флоранс Маснада | |
| Супергигант, женщины |  Пикабо Стрит Пикабо Стрит |  Михаэла Дорфмайстер Михаэла Дорфмайстер |  Александра Майсснитцер Александра Майсснитцер | |
| Слалом-гигант, женщины |  Дебора Компаньони Дебора Компаньони |  Александра Майсснитцер Александра Майсснитцер |  Катя Зайцингер Катя Зайцингер | |
| Слалом, женщины |  Хильде Герг Хильде Герг |  Дебора Компаньони Дебора Компаньони |  Зали Стегалл Зали Стегалл | |
| Комбинация, женщины |  Катя Зайцингер Катя Зайцингер |  Мартина Эртль Мартина Эртль |  Хильде Герг Хильде Герг | |
| Биатлон (Нодзаваонсен) | спринт, мужчины |  Уле-Эйнар Бьёрндален Уле-Эйнар Бьёрндален |  Фруде Андресен Фруде Андресен |  Вилле Ряйккёнен Вилле Ряйккёнен |
| Индивидуальная гонка, 20 км, мужчины |  Халвар Ханевольд Халвар Ханевольд |  Пьер Альберто Каррара Пьер Альберто Каррара |  Алексей Айдаров Алексей Айдаров | |
| Эстафета, 4x7,5, мужчины | Германия |
www.wikiznanie.ru
Зимние Олимпийские игры 1998 - WikiVisually
1. Нагано – Nagano is the capital city of Nagano Prefecture in the Chūbu region of Japan. As of 1 October 2016, the city had an population of 375,234. Its total area was 834.81 square kilometres, during the Sengoku period, the area was hotly contested between the forces of the Uesugi clan based in Echigo Province and the Takeda clan based in Kai Province. The several Battles of Kawanakajima between Uesugi Kenshin and Takeda Shingen were fought near here, during the Edo period, much of the area came under the control of the Sanada clan based at Matsushiro Domain. The area suffered from flooding in 1742, and from a earthquake in 1847. Following the Meiji restoration and the creation of the system on April 1,1889. Nagano was elevated to city status on April 1,1897 and it was the first city founded in Nagano Prefecture and the 43rd city in Japan. The city borders expanded on July 1,1923, with the annexation of the town of Yoshida and villages of Sarita, Miwa. The city again expanded on April 1,1954 by annexing neighbouring villages of Asahi, Furusato, Yanagihara, Wakatsuki, Asakawa, Naganuma, Amori, Odagiri, Imoi and Mamejima. In 1959, due to the flooding of Chikuma River,71 people died or were missing and 20,000 homes were flooded. On October 16,1966, the city expanded by annexing the neighbouring towns of Kawanakajima, Matsushiro and Wakaho, and villages of Shinonoi, Kohoku, Shinko. During the 1985 Matsushiro earthquake,27 people died and 60 homes were destroyed or badly damaged due to landslides, in 1998, Nagano hosted the 1998 Winter Olympics and the Paralympics. It was elevated to a city with increased local autonomy in 1999. Nagano continued to expand on January 1,2005, by absorbing the municipalities of Toyono, and the village of Togakushi, and Kinasa, Nagano hosted the 2005 Special Olympics World Winter Games. On January 1,2010, Nagano absorbed the town of Shinshūshinmachi, as of 2010, Nagano was the southernmost host of the Winter Olympic Games. The Nagano Olympic Commemorative Marathon is held annually to commemorate the occasion, Nagano is located in north-central Nagano Prefecture, near the confluence of the Chikuma River and the Sai River. The city receives heavy winter snow totaling 2.57 metres from December to March, the city has 12 public high schools operated by the Nagano Prefectural Board of Education, one public high school operated by the city government, and five private high schools. In addition, the city has four special education schools, the citys main railway hub, Nagano Station, and the smaller Shinonoi Station, were expanded for the Olympics
2. Япония – Japan is a sovereign island nation in Eastern Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies off the eastern coast of the Asia Mainland and stretches from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea, the kanji that make up Japans name mean sun origin. 日 can be read as ni and means sun while 本 can be read as hon, or pon, Japan is often referred to by the famous epithet Land of the Rising Sun in reference to its Japanese name. Japan is an archipelago consisting of about 6,852 islands. The four largest are Honshu, Hokkaido, Kyushu and Shikoku, the country is divided into 47 prefectures in eight regions. Hokkaido being the northernmost prefecture and Okinawa being the southernmost one, the population of 127 million is the worlds tenth largest. Japanese people make up 98. 5% of Japans total population, approximately 9.1 million people live in the city of Tokyo, the capital of Japan. Archaeological research indicates that Japan was inhabited as early as the Upper Paleolithic period, the first written mention of Japan is in Chinese history texts from the 1st century AD. Influence from other regions, mainly China, followed by periods of isolation, from the 12th century until 1868, Japan was ruled by successive feudal military shoguns who ruled in the name of the Emperor. Japan entered into a period of isolation in the early 17th century. The Second Sino-Japanese War of 1937 expanded into part of World War II in 1941, which came to an end in 1945 following the bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Japan is a member of the UN, the OECD, the G7, the G8, the country has the worlds third-largest economy by nominal GDP and the worlds fourth-largest economy by purchasing power parity. It is also the worlds fourth-largest exporter and fourth-largest importer, although Japan has officially renounced its right to declare war, it maintains a modern military with the worlds eighth-largest military budget, used for self-defense and peacekeeping roles. Japan is a country with a very high standard of living. Its population enjoys the highest life expectancy and the third lowest infant mortality rate in the world, in ancient China, Japan was called Wo 倭. It was mentioned in the third century Chinese historical text Records of the Three Kingdoms in the section for the Wei kingdom, Wa became disliked because it has the connotation of the character 矮, meaning dwarf. The 倭 kanji has been replaced with the homophone Wa, meaning harmony, the Japanese word for Japan is 日本, which is pronounced Nippon or Nihon and literally means the origin of the sun. The earliest record of the name Nihon appears in the Chinese historical records of the Tang dynasty, at the start of the seventh century, a delegation from Japan introduced their country as Nihon
3. Акихито – Akihito is the reigning Emperor of Japan. He is the 125th emperor of his line according to Japans traditional order of succession, Akihito succeeded his father Shōwa and acceded to the Chrysanthemum Throne on 7 January 1989. There has been ongoing coverage of his possible abdication due to age,31 December 2018 and 1 January 2019 has been mentioned as possible dates of such abdication. In Japan, the Emperor is never referred to by his given name, in writing, the Emperor is also referred to formally as The Reigning Emperor. The Era of Akihitos reign bears the name Heisei, and according to custom he will be renamed Emperor Heisei by order of the Cabinet after his death, at the same time, the name of the next era under his successor will also be established. Akihito was born in the Tokyo Imperial Palace, Tokyo City, Japan, and is the elder son and the fifth child of the Emperor Shōwa and Empress Kōjun. Titled Prince Tsugu as a child, he was raised and educated by his private tutors, unlike his predecessors in the Imperial family, he did not receive a commission as an army officer, at the request of his father, Hirohito. During the American firebombing raids on Tokyo in March 1945, Akihito and his younger brother, during the American occupation of Japan following World War II, Prince Akihito was tutored in the English language and Western manners by Elizabeth Gray Vining. He briefly studied at the Department of Political Science at Gakushuin University in Tokyo, Akihito was heir-apparent to the Chrysanthemum Throne from the moment of his birth. His formal Investiture as Crown Prince was held at the Tokyo Imperial Palace on 10 November 1952, in June 1953 Akihito represented Japan at the Coronation of Queen Elizabeth II in London. Crown Prince Akihito and Crown Princess Michiko made official visits to thirty-seven countries, upon the death of Emperor Hirohito on 7 January 1989, his eldest son the Crown Prince Akihito succeeded to the throne, with an enthronement ceremony taking place on 12 November 1990. In 1998, during a visit to the United Kingdom. Emperor Akihito underwent surgery for cancer on 14 January 2003. Since succeeding to the throne, Emperor Akihito has made an effort to bring the Imperial family closer to the Japanese people, the Emperor and Empress of Japan have made official visits to eighteen countries and to all forty-seven Prefectures of Japan. The Emperor and Empress also made a visit on Wednesday,30 March 2011 to a temporary shelter housing refugees of the disaster and this kind of event is also extremely rare, though in line with the Emperors attempts to bring the Imperial family closer to the people. Later in 2011 he was admitted to suffering from pneumonia. In February 2012 it was announced that the Emperor would be having a coronary examination, however, senior officials within the Imperial Household Agency have denied that there is any official plan for the monarch to abdicate. A potential abdication by the Emperor would require an amendment to the Imperial Household Act, on 8 August 2016, the Emperor gave a rare televised address, where he emphasized his advanced age and declining health, this address is interpreted as an implication of his intention to abdicate
4. Олимпийский огонь – The Olympic flame is a symbol of the Olympic Games. Commemorating the theft of fire from the Greek god Zeus by Prometheus, its origins lie in ancient Greece, the fire was introduced at the Games of the IX Olympiad 1928 in Amsterdam and it has been part of the modern Olympic Games ever since. The first fire of the Olympic Winter Games was introduced at the IV Olympic Winter Games 1936 in Garmisch-Partenkirchen, the Olympic Torch today is ignited several months before the opening ceremony of the Olympic Games at the site of the ancient Olympics in Olympia, Greece. Eleven women, representing the Vestal Virgins, perform a celebration at the Temple of Hera in which the torch is kindled by the light of the Sun, its rays concentrated by a parabolic mirror. The torch briefly travels around Greece via short relay, and then starts its transfer to the host city after a ceremony in the Panathenaic Stadium in Athens, the Olympic Torch Relay ends on the day of the opening ceremony in the central stadium of the Games. The final carrier is often kept unannounced until the last moment, the final bearer of the torch runs towards the cauldron, often placed at the top of a grand staircase, and then uses the torch to start the flame in the arena. It is considered to be an honor to be asked to light the Olympic flame. After being lit, the continues to burn throughout the Games, until the day of the closing ceremony and celebration. In the time of the games within the boundaries of Olympia. For the ancient Greeks, fire had divine connotations—it was thought to have stolen from the gods by Prometheus. Therefore, fire was present at many of the sanctuaries in Olympia. During the Olympic Games, which honoured Zeus, additional fires were lit at his temple, the modern Olympic flame is ignited at the site where the temple of Hera used to stand. The tradition was reintroduced during the 1928 Games, an employee of the Electric Utility of Amsterdam lit the first Olympic flame in the Marathon Tower of the Olympic Stadium in Amsterdam. The modern convention of moving the Olympic flame via a system from Greece to the Olympic venue began in 1936 in Germany. Carl Diem devised the idea of the relay for the 1936 Summer Olympics in Berlin that was organized by the Nazis under the guidance of Joseph Goebbels. The Krupp armaments company produced the torches in wood and metal, the Olympic flame was lit by a concave mirror in Olympia, Greece and transported over 3,187 kilometres by 3,331 runners in twelve days and eleven nights from Greece to Berlin. Leni Riefenstahl later staged the torch relay for the 1938 film Olympia, adolf Hitler saw the link with the ancient Games as the perfect way to illustrate his belief that classical Greece was an Aryan forerunner of the modern German Reich. There were minor protests in Yugoslavia and Czechoslovakia on the way, although most of the time the torch with the Olympic flame is still carried by runners, it has been transported in many different ways
5. Главные стадионы Олимпийских игр – Olympic Stadium is the name usually given to the main stadium of an Olympic Games. An Olympic stadium is the site of the opening and closing ceremonies, many, though not all, of these venues actually contain the words Olympic Stadium as part of their names. Olympic Stadium may also be named a stadium which hosts Olympic sports. In the case of the Summer Olympics, athletics competitions and the final are traditionally held in the Olympic Stadium. Exceptions to this have occurred though at the 1900,1996 and 2016 Summer Olympics as well as at the 2010 and 2018 Summer Youth Olympic Games, early Winter Games often used figure skating venues as focal points. These were often designated as the Olympic Stadium, usually hosting the opening and closing ceremonies, a number of stadiums have been used in more than one Olympics, in those cities that have held the Games more than once. Lysgårdsbakkene was the stadium of a Winter Olympics and a Winter Youth Olympic Games. Bergiselschanze was the stadium of two Winter Olympics and one Winter YOG. Olympiahalle jointly shared the Olympic Stadium role with Bergiselschanze during the two Winter Olympics, but not during the Winter YOG, only one stadium, the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum, has been the main stadium of two Summer Olympics. In addition to the inaugural Summer Olympics, Panathinaiko Stadio was also the stadium of the only Intercalated Games held. A number, including both the Panathinaiko Stadio and the Vélodrome de Vincennes, have hosted events at subsequent Olympics. The London Games of 2012 were not opened and closed at the rebuilt Wembley Stadium, the site of the 1948 Olympic Stadium, Wembley was, however, the venue for some 2012 Olympic football matches. Likewise, the Melbourne Cricket Ground, which was the stadium for the 1956 games. Lake Placids 1930 Olympic Stadium was utilized in the 1980 Lake Placid games as the speed skating venue, olympiahalle hosted figure skating and short-track speed skating during the 2012 Winter Youth Olympics. Stockholm Olympic Stadium hosted equestrian events for the 1956 Summer Olympics, Olympic Past & Future Stadiums - BALLPARKS. com Summer Olympic Stadiums 1896 - on Google Maps
6. Зимние Олимпийские игры 1994 – The 1994 Winter Olympics, officially known as the XVII Olympic Winter Games, was a winter multi-sport event celebrated from 12 to 27 February 1994 in and around Lillehammer, Norway. Lillehammer failed to win the bid for the 1992 event, Lillehammer was awarded the 1994 Winter Olympics in 1988, after beating Anchorage, United States, Östersund, Sweden, and Sofia, Bulgaria. Lillehammer is the northernmost city to ever host the Winter Games, while many events took place in Lillehammer, skating took place in Hamar, some ice hockey matches were placed in Gjøvik, while Alpine skiing was held in Øyer and Ringebu. Sixty-seven countries and 1,737 athletes participated in six sports, fourteen countries made their debut in the Winter Olympics, of which nine were former Soviet republics. The Games also saw the introduction of stricter qualifying rules, reducing the number of under-performing participants from warm-weather countries, new events were two new distances in short track speed skating and aerials, while speed skating was moved indoors. Nearly two million people spectated the games, which were the first to have the Olympic truce in effect, the games were succeeded by the 1994 Winter Paralympics from 10 to 19 March. Manuela Di Centa and Lyubov Yegorova dominated womens cross-country skiing, taking five and four medals, a crowd of over 100,000 saw Italy beat Norway by 0.4 seconds on the mens 4 x 10 km relay. Vreni Schneider won a set of medals in Alpine skiing. Nancy Kerrigan had, before the games, been clubbed by Tonya Hardings associate, Johann Olav Koss won three speed skating events, while 13-year-old Kim Yoon-Mi became the youngest-ever Olympic gold medalist. Sweden beat Canada in a penalty shootout in the ice hockey final. With 11 gold medals, Russia won the most events, while with 26, planning of the Lillehammer bid started in 1981, following Falun, Swedens failed bid for the 1988 Winter Olympics. It was supported by the government largely to help stimulate the economy of the inland counties, Lillehammer originally bid for the 1992 Games, but came fourth in the voting. A new bid was launched for the 1994 Games, modified with an speed skating venue. Three other locations bid for the games, Östersund, Anchorage, the 94th IOC Session, held in Seoul on 15 September 1988, voted Lillehammer the host for the Games. The Lillehammer Olympics were the last Winter Games to date to be held in a town,1.21 million tickets were sold for the games. LOOC estimated that an additional 500,000 viewed the games for free along the courses, in addition,180,000 seats were used by the media and VIPs. The overall responsibility for the games was held by the Lillehammer Olympic Organizing Committee, the government had issued a guarantee for the games, and also covered the expenses related to infrastructure. The games had a revenue of NOK2.71 billion, of which NOK1.43 billion was from television rights, NOK0.65 billion was from sponsors, and NOK0.15 billion was from ticket sales
7. Зимние Олимпийские игры 2002 – Approximately 2,400 athletes from 78 nations participated in 78 events in fifteen disciplines, held throughout 165 sporting sessions. The 2002 Winter Olympics and the 2002 Paralympic Games were both organized by the Salt Lake Organizing Committee, Utah became the fifth state in the United States to host the Olympic Games, and the 2002 Winter Olympics are the most recent games to be held in the United States. These were the first Olympic Games under the IOC presidency of Jacques Rogge, the opening ceremony was held on February 8,2002, and sporting competitions were held up until the closing ceremony on February 24,2002. Production for both ceremonies was designed by Seven Nielsen, and music for both ceremonies was directed by Mark Watters, Salt Lake City became the most populous area ever to have hosted the Winter Olympics, although the two subsequent host cities populations were larger. Following a trend, the 2002 Olympic Winter Games were also larger than all prior Winter Games, with 10 more events than the 1998 Winter Olympics in Nagano, Japan. The Salt Lake Games faced a scandal and some local opposition during the bid. Nevertheless, from sporting and business standpoints, this was one of the most successful Winter Olympiads in history, over 2 billion viewers watched more than 13 billion viewer-hours. The Games were also financially successful raising more money with fewer sponsors than any prior Olympic Games, the surplus was used to create the Utah Athletic Foundation, which maintains and operates many of the remaining Olympic venues. U. S. Federal subsidies amounted to $1.3 billion, Salt Lake City was chosen over Québec City, Canada, Sion, Switzerland, and Östersund, Sweden, on June 16,1995, at the 104th IOC Session in Budapest, Hungary. The 1976 Winter Olympics were ultimately awarded to Innsbruck, Austria, 1Because of the no-commercialization policy of the Olympics, the Delta Center, now the Vivint Smart Home Arena, was labeled as the Salt Lake Ice Center, causing some confusion for visitors. The Oxford Olympics Study established the outturn cost of the Salt Lake City 2002 Winter Olympics at USD2.5 billion in 2015-dollars and cost overrun at 24% in real terms. This includes sports-related costs only, that is, operational costs incurred by the committee for the purpose of staging the Games. The competition venues, the Olympic village, international broadcast center, and media and press center, average cost for Winter Games since 1960 is USD3.1 billion, average cost overrun is 142%. A total 78 National Olympic Committees sent athletes to the Salt Lake City games, cameroon, Hong Kong, Nepal, Tajikistan, and Thailand participated in their first Winter Olympic Games. There were 78 events contested in 7 sports, in the following calendar for the 2002 Winter Olympic Games, each blue box represents an event competition, such as a qualification round, on that day. The yellow boxes represent days during which medal-awarding finals for a sport are held, the number in each box represents the number of finals that were contested on that day. All dates are in Mountain Standard Time Host country To sort this table by nation, total medal count, or any other column, several medals records were set and/or tied. They included, Norway tied the Soviet Union at the 1976 Winter Olympics for most gold medals at a Winter Olympics, germany set a record for most total medals at a Winter Olympics, with 36
8. Аоста – Aosta is the principal city of Aosta Valley, a bilingual region in the Italian Alps,110 km north-northwest of Turin. It is situated near the Italian entrance of the Mont Blanc Tunnel, at the confluence of the Buthier and the Doire baltée, Aosta is not the capital of the province, because Aosta Valley is the only Italian region not divided into provinces. Provincial administrative functions are shared by the region and the communes. Aosta was settled in times and later became a centre of the Salassi. The campaign was led by Terentius Varro, who founded the Roman colony of Augusta Praetoria Salassorum. After 11 BC Aosta became the capital of the Alpes Graies province of the Empire. Its position at the confluence of two rivers, at the end of the Great and the Little St Bernard Pass, gave it military importance. After the fall of the Western Empire, the city was conquered, in turn, by the Burgundians, the Ostrogoths, the Lombards, who had annexed it to their Italian kingdom, were expelled by the Frankish Empire under Pepin the Short. Under his son, Charlemagne, Aosta acquired importance as a post on the Via Francigena, after 888 AD it was part of the renewed Kingdom of Italy under Arduin of Ivrea and Berengar of Friuli. In the 10th century Aosta became part of the Kingdom of Burgundy, after the fall of the latter in 1032, it became part of the lands of Count Humbert I of Savoy. The ancient town walls of Augusta Prætoria Salassorum are still preserved almost in their entirety and they are 6.4 metres high, built of concrete faced with small blocks of stone. At the bottom, the walls are nearly 2.75 metres thick, towers stand at angles to the enceinte and others are positioned at intervals, with two at each of the four gates, making twenty towers in total. They are roughly 6.5 metres square, and project 4.3 metres from the wall. Of the 20 original towers, the following are well preserved, Le lépreux de la cité dAoste, a novel by Xavier de Maistre, is also named after this leper. Tower of Bramafan, built in the 11th century over a Roman bastion and it was the residence of the Savoy viscounts. The Franco-Provençal term Bramafan is translated as He who screams for hunger, the east and south gates exist intact. The latter, a gate with three arches flanked by two towers known as the Porta Praetoria was the eastern gate to the city, and has preserved its original forms apart from the marble covering. It is formed by two series of arches enclosing a small square, the rectangular arrangement of the streets is modeled on a Roman plan dividing the town into 64 blocks
9. Хака (город) – Jaca is a city of northeastern Spain in the province of Huesca, located near the Pyrenees and the border with France. Jaca is an ancient fort on the Aragón River, situated at the crossing of two early medieval routes, one from Pau to Zaragoza. Jaca was the city out of which the County and Kingdom of Aragon developed It was the capital of Aragon until 1097, besides Jaca town, there are a number of outlying villages in Jacas municipality, including the ski resort of Astún. The origins of the city are obscure, but its name is apparently of Lacetani origin, Strabo adds that their territory lay on the site of the wars in the 1st century BC between Sertorius and Pompey. The coins show a bearded head to the right with an inscription to the left. The reverse side depicts a horseman carrying a spear to the right and it is unknown when the town was reconquered. Ramiro I of Aragon granted it the title of City, in 1063 it was the site of the Synod of Jaca. On December 12–131930 a mutiny, demanding the abolition of the monarchy, was suppressed with some difficulty and it was an early event that preceded the Spanish Civil War. Jaca boasts several medieval walls and towers surrounding the 11th-century Romanesque Jaca Cathedral, the Jaca citadel, a fortification dating to the late 16th century, is home to a colony of rock sparrows. The Diocesan Museum of Jaca protects Romanesque and Gothic frescoes, some of which were found in the most remote locations in the Jaca district, Jaca is a tourist destination in the region for summer holidays and winter sports. Jaca was the host city of the 1981 and 1995 Winter Universiades, the city also hosted the 2007 European Youth Olympic Winter Festival. Its popularity for winter sports has been a factor in the citys failed bids for the 1998 Winter Olympics,2002 Winter Olympics and 2010 Winter Olympics. It was again the applicant city of Spain for the 2014 Winter Olympics, diocese of Jaca Official website Diocesan Museum of Jaca Jaca, Useful information about tourism and lodgings
wikivisually.com
Зимние Олимпийские игры 1998 — Википедия
XVIII зимние Олимпийские игры проводились в японском городе Нагано в период с 7 февраля по 22 февраля 1998 года. Другими кандидатами на проведение игр были итальянская Аоста, шведский Эстерсунд, испанская Хака, Солт-Лейк-Сити (США). По общему мнению, сложная победа (46:42 в последнем туре голосования) над Солт-Лейк-Сити досталась Нагано за счет «фактора Атланты» — то есть благодаря тому, что летние ОИ 1996 уже были отданы США.
Нагано стал самым близким к экватору городом, принимавшим Зимние игры, и остаётся им до сих пор.
Итоги Олимпийских игр[править]
| Горные лыжи (Яманоути/Якэбитай/Хаукба) | Скоростной спуск, мужчины |  Жан-Люк Кретье Жан-Люк Кретье |  Лассе Чьюс Лассе Чьюс |  Ханнес Тринкль Ханнес Тринкль |
| Супергигант, мужчины |  Херманн Майер Херманн Майер |  Дидье Кюш, Дидье Кюш,  Ханс Кнаусс Ханс Кнаусс | ||
| Слалом-гигант, мужчины |  Херманн Майер Херманн Майер |  Штефан Эберхартер Штефан Эберхартер |  Михаэль фон Грюниген Михаэль фон Грюниген | |
| Слалом, мужчины |  Ханс Петтер Бурос Ханс Петтер Бурос |  Уле Кристиан Фурусет Уле Кристиан Фурусет |  Томас Сикора Томас Сикора | |
| Комбинация, мужчины |  Марио Райтер Марио Райтер |  Лассе Чьюс Лассе Чьюс |  Кристиан Майер Кристиан Майер | |
| Скоростной спуск, женщины |  Катя Зайцингер Катя Зайцингер |  Пернилла Виберг Пернилла Виберг |  Флоранс Маснада Флоранс Маснада | |
| Супергигант, женщины |  Пикабо Стрит Пикабо Стрит |  Михаэла Дорфмайстер Михаэла Дорфмайстер |  Александра Майсснитцер Александра Майсснитцер | |
| Слалом-гигант, женщины |  Дебора Компаньони Дебора Компаньони |  Александра Майсснитцер Александра Майсснитцер |  Катя Зайцингер Катя Зайцингер | |
| Слалом, женщины |  Хильде Герг Хильде Герг |  Дебора Компаньони Дебора Компаньони |  Зали Стегалл Зали Стегалл | |
| Комбинация, женщины |  Катя Зайцингер Катя Зайцингер |  Мартина Эртль Мартина Эртль |  Хильде Герг Хильде Герг | |
| Биатлон (Нодзаваонсен) | спринт, мужчины |  Уле-Эйнар Бьёрндален Уле-Эйнар Бьёрндален |  Фруде Андресен Фруде Андресен |  Вилле Ряйккёнен Вилле Ряйккёнен |
| Индивидуальная гонка, 20 км, мужчины |  Халвар Ханевольд Халвар Ханевольд |  Пьер Альберто Каррара Пьер Альберто Каррара |  Алексей Айдаров Алексей Айдаров | |
| Эстафета, 4x7,5, мужчины | Германия Германия ( Германия ( |
www.wikiznanie.ru
1998 зимние Олимпийские игры - это... Что такое 1998 зимние Олимпийские игры?
1998 зимние Олимпийские игрыWikimedia Foundation. 2010.
- 19P/Борелли
- 19 Fortuna
Смотреть что такое "1998 зимние Олимпийские игры" в других словарях:
Зимние Олимпийские игры 2022 — (англ. 2022 Winter Olympics, фр. Jeux Olympiques d’hiver de 2022, официальное название XXIV Зимние Олимпийские игры) 24 е по счёту зимние Олимпийские игры, которые пройдут в начале 2022 года. Официальные заявки на проведения Игр… … Википедия
Зимние Олимпийские игры 1940 — года первоначально должны были пройти с 3 по 12 февраля 1940 года в Саппоро, Япония. После отказа Японии проводить игры, МОК в июле 1937 года перенёс запланированные игры в Санкт Мориц, однако позднее из за разногласий со швейцарским комитетом… … Википедия
Зимние Олимпийские игры — Места проведения зимних Олимпийских игр … Википедия
Зимние Олимпийские игры 2010 — XXI зимние Олимпийские игры Город организатор Ванкувер, Британская Колумбия, Канада … Википедия
Зимние Олимпийские Игры — Места проведения зимних Олимпийских игр Зимние Олимпийские игры крупнейшие международные соревнования по зимним видам спорта, проводящиеся один раз в 4 года под эгидой Международного олимпийского комитета. Зимние Олимпийские игры начали… … Википедия
Зимние Олимпийские игры 2026 — Места проведения зимних Олимпийских игр Зимние Олимпийские игры крупнейшие международные соревнования по зимним видам спорта, проводящиеся один раз в 4 года под эгидой Международного олимпийского комитета. Зимние Олимпийские игры начали… … Википедия
Зимние олимпийские игры — Места проведения зимних Олимпийских игр Зимние Олимпийские игры крупнейшие международные соревнования по зимним видам спорта, проводящиеся один раз в 4 года под эгидой Международного олимпийского комитета. Зимние Олимпийские игры начали… … Википедия
Зимние Олимпийские игры 1998 — XVIII зимние Олимпийские игры Город организатор Нагано, Япония Страны участницы 72 … Википедия
Зимние Олимпийские игры 2018 — Эта статья или раздел содержит информацию о предстоящем спортивном событии, которое состоится через 5 лет 1 месяц 15 дней. С началом события содержание статьи, возможно, будет изменятьс … Википедия
Зимние Олимпийские игры 2014 — Эта статья или раздел содержит информацию о предстоящем спортивном событии, которое состоится через 1 год 1 месяц 16 дней. С началом события содержание статьи, возможно, будет изменятьс … Википедия
dic.academic.ru





