Хисамутдинов, Шамиль Шамшатдинович. Шамиль хисамутдинов википедия
Хисамутдинов, Шамиль Шамшатдинович — Википедия
Материал из Википедии — свободной энциклопедии
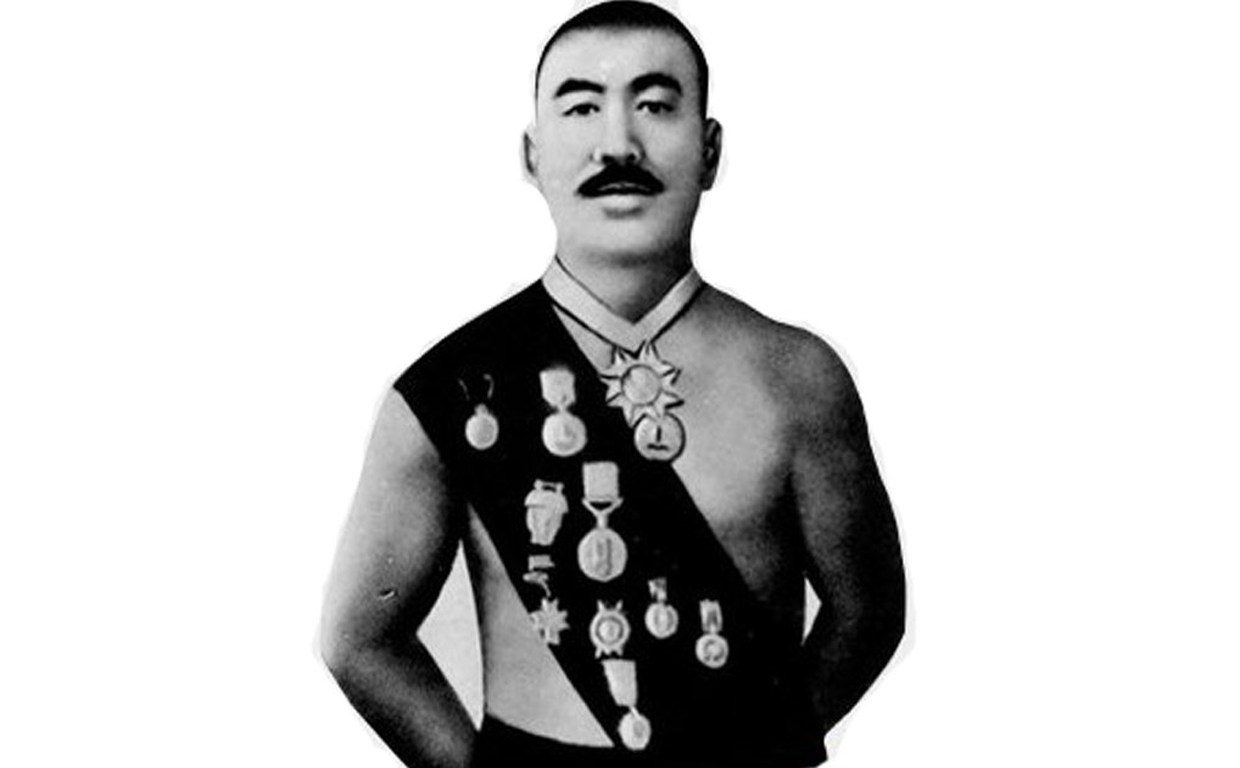
Шами́ль Шамшатди́нович Хисамутди́нов (тат. Шамил Шәмсетдин улы Хисаметдинов; род. 20 сентября 1950, Узловая, Тульская область, СССР) — советский борец классического (греко-римского) стиля. Заслуженный мастер спорта СССР (1972). Заслуженный тренер СССР (1978). Олимпийский чемпион в первом полусреднем весе (1972)[1], чемпион мира (1973, 1975)[2], чемпион Европы (1973, 1974)[2], бронзовый призёр чемпионата Европы (1976)[2], чемпион СССР (1971—1974).
Родился 20 сентября 1950 года в Узловой Тульской области в семье шахтера и домохозяйки. Окончил узловскую среднюю школу № 17 и Омский институт физической культуры (1977). В детстве занимался многими видами спорта: бег, лапта, футбол, баскетбол, теннис. Первый титул — чемпион города по лыжам.
Воспитанник детской спортивной школы в Узловой. В 1968 году переехал в Тулу, где стал заниматься борьбой в ДСО «Труд» у Анатолия Белоусова. С 1972 по 1974 год выступал за «Спартак» (Московская область). На победной для себя Олимпиаде в Мюнхене Хисамутдинов выиграл чистым туше четыре схватки из шести. В 1976 году на чемпионате Европы в Ленинграде получил серьёзную травму плеча, ставшую причиной преждевременного завершения карьеры. Член КПСС с 1976 года. В 26 лет был назначен главным тренером сборной СССР по борьбе. Работал со сборной Швеции по этому виду спорта. 29 января 2010 года избран на четырехлетний срок президентом Всероссийской федерации борьбы на поясах (ВФБП).
С 1996 года живёт в пос. Новогромово Подольского района.
Награждён орденами «Знак Почёта» (1976), «Почёта» (2000), медалью «За трудовую доблесть» (1996).
Один из двух братьев Хисамутдинова, Михаил (1948), был нападающим футбольных команд мастеров «Металлург» (Тула) и «Химик» (Новомосковск).
ru.wikiyy.com
Хисамутдинов, Шамиль Шамшатдинович - WikiVisually
1. Союз Советских Социалистических Республик – The Soviet Union, officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics was a socialist state in Eurasia that existed from 1922 to 1991. It was nominally a union of national republics, but its government. The Soviet Union had its roots in the October Revolution of 1917 and this established the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and started the Russian Civil War between the revolutionary Reds and the counter-revolutionary Whites. In 1922, the communists were victorious, forming the Soviet Union with the unification of the Russian, Transcaucasian, Ukrainian, following Lenins death in 1924, a collective leadership and a brief power struggle, Joseph Stalin came to power in the mid-1920s. Stalin suppressed all opposition to his rule, committed the state ideology to Marxism–Leninism. As a result, the country underwent a period of rapid industrialization and collectivization which laid the foundation for its victory in World War II and postwar dominance of Eastern Europe. Shortly before World War II, Stalin signed the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact agreeing to non-aggression with Nazi Germany, in June 1941, the Germans invaded the Soviet Union, opening the largest and bloodiest theater of war in history. Soviet war casualties accounted for the highest proportion of the conflict in the effort of acquiring the upper hand over Axis forces at battles such as Stalingrad. Soviet forces eventually captured Berlin in 1945, the territory overtaken by the Red Army became satellite states of the Eastern Bloc. The Cold War emerged by 1947 as the Soviet bloc confronted the Western states that united in the North Atlantic Treaty Organization in 1949. Following Stalins death in 1953, a period of political and economic liberalization, known as de-Stalinization and Khrushchevs Thaw, the country developed rapidly, as millions of peasants were moved into industrialized cities. The USSR took a lead in the Space Race with Sputnik 1, the first ever satellite, and Vostok 1. In the 1970s, there was a brief détente of relations with the United States, the war drained economic resources and was matched by an escalation of American military aid to Mujahideen fighters. In the mid-1980s, the last Soviet leader, Mikhail Gorbachev, sought to reform and liberalize the economy through his policies of glasnost. The goal was to preserve the Communist Party while reversing the economic stagnation, the Cold War ended during his tenure, and in 1989 Soviet satellite countries in Eastern Europe overthrew their respective communist regimes. This led to the rise of strong nationalist and separatist movements inside the USSR as well, in August 1991, a coup détat was attempted by Communist Party hardliners. It failed, with Russian President Boris Yeltsin playing a role in facing down the coup. On 25 December 1991, Gorbachev resigned and the twelve constituent republics emerged from the dissolution of the Soviet Union as independent post-Soviet states
2. Россия – Russia, also officially the Russian Federation, is a country in Eurasia. The European western part of the country is more populated and urbanised than the eastern. Russias capital Moscow is one of the largest cities in the world, other urban centers include Saint Petersburg, Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg, Nizhny Novgorod. Extending across the entirety of Northern Asia and much of Eastern Europe, Russia spans eleven time zones and incorporates a range of environments. It shares maritime borders with Japan by the Sea of Okhotsk, the East Slavs emerged as a recognizable group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries AD. Founded and ruled by a Varangian warrior elite and their descendants, in 988 it adopted Orthodox Christianity from the Byzantine Empire, beginning the synthesis of Byzantine and Slavic cultures that defined Russian culture for the next millennium. Rus ultimately disintegrated into a number of states, most of the Rus lands were overrun by the Mongol invasion. The Soviet Union played a role in the Allied victory in World War II. The Soviet era saw some of the most significant technological achievements of the 20th century, including the worlds first human-made satellite and the launching of the first humans in space. By the end of 1990, the Soviet Union had the second largest economy, largest standing military in the world. It is governed as a federal semi-presidential republic, the Russian economy ranks as the twelfth largest by nominal GDP and sixth largest by purchasing power parity in 2015. Russias extensive mineral and energy resources are the largest such reserves in the world, making it one of the producers of oil. The country is one of the five recognized nuclear weapons states and possesses the largest stockpile of weapons of mass destruction, Russia is a great power as well as a regional power and has been characterised as a potential superpower. The name Russia is derived from Rus, a state populated mostly by the East Slavs. However, this name became more prominent in the later history, and the country typically was called by its inhabitants Русская Земля. In order to distinguish this state from other states derived from it, it is denoted as Kievan Rus by modern historiography, an old Latin version of the name Rus was Ruthenia, mostly applied to the western and southern regions of Rus that were adjacent to Catholic Europe. The current name of the country, Россия, comes from the Byzantine Greek designation of the Kievan Rus, the standard way to refer to citizens of Russia is Russians in English and rossiyane in Russian. There are two Russian words which are translated into English as Russians
3. Спартак (спортивное общество) – Spartak is an international fitness and sports society that unites some countries of the former Soviet Union. It was founded in 1921 in Moscow as the Moscow Sports Circle by footballer Nikolai Starostin, in 1926 it came under the sponsorship of the food workers union. In 1934, it adopted the name of Spartak, after the ancient Roman slave, rebel and athlete Spartacus and it was dissolved in 1987 and reformed in 1991 as an international society among six nations of the former Soviet Union. Spartak was the first and the largest All-Union Voluntary Sports Society of workers of state trade, producers cooperation, light industry, civil aviation, education, culture, in 1936 Spartak organized and successfully conducted a sports parade at the Moscows Red Square. In 1960 the society was reorganized into the Voluntary Sport Society, there were 23,000 physical culture collectives in the society in 1975, that united 6.2 million people. There were 40 sports disciplines cultivated in the society in 1975, the society possessed 238 stadiums,89 swimming pools,1,800 sports halls,1,300 football grounds,2,600 sports camps,264 Children and Youth Sport Schools. In 1987 Spartak was abolished and all its assets were transferred back to trade unions, in 1991 the society was reorganized as an international. Currently the society has affiliation in six countries of the former Soviet Union, Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, Nikolai Starostin Semyon Privis Gennadiy Mikhalchuk Pyotr Sobolev Yevgeniy Arkhipov Vladimir Vekshin Nikolai Ozerov Anna Alyoshina VSS Spartak was awarded Order of Lenin
4. Узловая – Uzlovaya is a town and the administrative center of Uzlovsky District in Tula Oblast, Russia. It was founded in 1873 as Khrushchyovskaya railway station and it was renamed Uzlovaya in 1877 and granted town status in 1938. The railway influenced much the life and the future of the town, within the framework of administrative divisions, Uzlovaya serves as the administrative center of Uzlovsky District. As an administrative division, it is incorporated within Uzlovsky District as Uzlovaya Town Under District Jurisdiction, as a municipal division, Uzlovaya Town Under District Jurisdiction is incorporated within Uzlovsky Municipal District as Uzlovaya Urban Settlement. The station connects three important railway directions, Ryazhsk, Yelets, and Tula, the first coal mines were founded in the late 1930s. Vasiliy Podshibyakin, geologist Тульская областная Дума, Закон №954-ЗТО от27 декабря2007 г. «Об административно-территориальном устройстве Тульской области», в ред, Закона №2131-ЗТО от11 июня2014 г. Вступил в силу по истечении десяти дней после дня официального опубликования, Опубликован, Вестник Тульской областной Думы, №11–12, часть4, ноябрь–декабрь2007 г. Закон №551-ЗТО от11 марта2005 г, Закона №1818-ЗТО от14 ноября2012 г. Вступил в силу через десять дней после официального опубликования, Опубликован, Тульские известия, №71–74,24 марта2005 г
5. Тульская область – Tula Oblast is a federal subject of Russia with its present borders formed on September 26,1937. Its administrative center is the city of Tula, the oblast has an area of 25,700 square kilometers and a population of 1,553,925. The current governor of the oblast is Alexey Dyumin, people have inhabited Tula area since ancient times, as shown by discoveries of burial mounds and old settlements. These lands were occupied by the Slavic Vyatichi tribe, who cultivated the land, traded and this is confirmed by records in property registers, which mention an ancient settlement located at the place where the small Tulitsa River flows into the Upa River. In those long-ago times, its inhabitants may also have defended their settlements against raids by Tatars and nomadic tribes, the first mention of Tula is found in Nikons chronicle in reference to the campaign of Prince Svyatoslav Olgovich of Chernigov. The chronicle notes that in 1146, the prince, who was heading for Ryazan, passed through a number of settlements, including Tula. Tula Oblast is located in Russias Central Federal District and borders Moscow, Ryazan, Lipetsk, Oryol, Tula Oblast contains more than 1,600 rivers and streams. Major rivers include, Don River Oka River Upa River The oblast is rich in ore, clay, limestone. The lignite deposit is part of the Moscow coal basin, Tula Oblast has a moderate continental climate, with warm summers and cold winters. Average January temperature is −10 °C in north and −9 °C in south, average July temperature is about +19 °C to +20 °C. Annual precipitation is 470 millimetres in southeast and 575 millimetres in northwest, since 1991, CPSU lost all the power, and the head of the Oblast administration, and eventually the governor was appointed/elected alongside elected regional parliament. The Charter of Tula Oblast is the law of the region. The Tula Oblast Duma is the provinces standing legislative body, the Oblast Duma exercises its authority by passing laws, resolutions, and other legal acts and by supervising the implementation and observance of the laws and other legal acts passed by it. It is estimated that the proportion of ethnicities in this group is the same as that of the declared group. In addition, 19% of the population declares to be spiritual but not religious, 13% is atheist, Tula Oblast is part of the Central economic region. It is a prominent industrial center with metalworking, engineering, coalmining, major industrial cities include Novomoskovsk and Aleksin. Historical industries, such as firearm, samovar, and accordion manufacturing, the oblast also has a developed agricultural sector, which ranks 33rd in Russia in agricultural production. The sector includes farming grain, potatoes, sugar beets, and vegetable growing, livestock raising, Tula Oblast has as many as 32 museums
wikivisually.com
Шамиль Шамшатдинович Хисамутдинов Вики
Шами́ль Шамшатди́нович Хисамутди́нов (тат. Шамил Шәмсетдин улы Хисаметдинов; род. 20 сентября 1950, Узловая, Тульская область, СССР) — советский борец классического (греко-римского) стиля. Заслуженный мастер спорта СССР (1972). Заслуженный тренер СССР (1978). Олимпийский чемпион в первом полусреднем весе (1972)[1], чемпион мира (1973, 1975)[2], чемпион Европы (1973, 1974)[2], бронзовый призёр чемпионата Европы (1976)[2], чемпион СССР (1971—1974).
Биография[ | код]
Родился 20 сентября 1950 года в Узловой Тульской области в семье шахтера и домохозяйки. Окончил узловскую среднюю школу № 17 и Омский институт физической культуры (1977). В детстве занимался многими видами спорта: бег, лапта, футбол, баскетбол, теннис. Первый титул — чемпион города по лыжам.
Воспитанник детской спортивной школы в Узловой. В 1968 году переехал в Тулу, где стал заниматься борьбой в ДСО «Труд» у Анатолия Белоусова. С 1972 по 1974 год выступал за «Спартак» (Московская область). На победной для себя Олимпиаде в Мюнхене Хисамутдинов выиграл чистым туше четыре схватки из шести. В 1976 году на чемпионате Европы в Ленинграде получил серьёзную травму плеча, ставшую причиной преждевременного завершения карьеры. Член КПСС с 1976 года. В 26 лет был назначен главным тренером сборной СССР по борьбе. Работал со сборной Швеции по этому виду спорта. 29 января 2010 года избран на четырехлетний срок президентом Всероссийской федерации борьбы на поясах (ВФБП).
С 1996 года живёт в пос. Новогромово Подольского района.
Награждён орденами «Знак Почёта» (1976), «Почёта» (2000), медалью «За трудовую доблесть» (1996).
Интересные факты[ | код]
Один из двух братьев Хисамутдинова, Михаил (1948), был нападающим футбольных команд мастеров «Металлург» (Тула) и «Химик» (Новомосковск).
Примечания[ | код]
Литература[ | код]
Ссылки[ | код]
ru.wikibedia.ru
Хисамутдинов, Шамиль Шамшатдинович Википедия
В Википедии есть статьи о других людях с фамилией Хисамутдинов.| Шамиль Хисамутдинов | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| мужской | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| СССР СССР → Россия Россия | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| «Труд», «Спартак» | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20 сентября 1950(1950-09-20) (67 лет) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Узловая, Тульская область, РСФСР, СССР | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1963—1976 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Николай Пархоменко | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| до 68 кг | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Награды и медали
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Шами́ль Шамшатди́нович Хисамутди́нов (тат. Шамил Шәмсетдин улы Хисаметдинов; род. 20 сентября 1950, Узловая, Тульская область, СССР) — советский борец классического (греко-римского) стиля. Заслуженный мастер спорта СССР (1972). Заслуженный тренер СССР (1978). Олимпийский чемпион в первом полусреднем весе (1972)[1], чемпион мира (1973, 1975)[2], чемпион Европы (1973, 1974)[2], бронзовый призёр чемпионата Европы (1976)[2], чемпион СССР (1971—1974).
ruwikiorg.ru
Хисамутдинов, Шамиль Шамшатдинович - Gpedia, Your Encyclopedia
Шами́ль Шамшатди́нович Хисамутди́нов (тат. Шамил Шәмсетдин улы Хисаметдинов; род. 20 сентября 1950, Узловая, Тульская область, СССР) — советский борец классического (греко-римского) стиля. Заслуженный мастер спорта СССР (1972). Заслуженный тренер СССР (1978). Олимпийский чемпион в первом полусреднем весе (1972)[1], чемпион мира (1973, 1975)[2], чемпион Европы (1973, 1974)[2], бронзовый призёр чемпионата Европы (1976)[2], чемпион СССР (1971—1974).
Биография
Родился 20 сентября 1950 года в Узловой Тульской области в семье шахтера и домохозяйки. Окончил узловскую среднюю школу № 17 и Омский институт физической культуры (1977). В детстве занимался многими видами спорта: бег, лапта, футбол, баскетбол, теннис. Первый титул — чемпион города по лыжам.
Воспитанник детской спортивной школы в Узловой. В 1968 году переехал в Тулу, где стал заниматься борьбой в ДСО «Труд» у Анатолия Белоусова. С 1972 по 1974 год выступал за «Спартак» (Московская область). На победной для себя Олимпиаде в Мюнхене Хисамутдинов выиграл чистым туше четыре схватки из шести. В 1976 году на чемпионате Европы в Ленинграде получил серьёзную травму плеча, ставшую причиной преждевременного завершения карьеры. Член КПСС с 1976 года. В 26 лет был назначен главным тренером сборной СССР по борьбе. Работал со сборной Швеции по этому виду спорта. 29 января 2010 года избран на четырехлетний срок президентом Всероссийской федерации борьбы на поясах (ВФБП).
С 1996 года живёт в пос. Новогромово Подольского района.
Награждён орденами «Знак Почёта» (1976), «Почёта» (2000), медалью «За трудовую доблесть» (1996).
Интересные факты
Один из двух братьев Хисамутдинова, Михаил (1948), был нападающим футбольных команд мастеров «Металлург» (Тула) и «Химик» (Новомосковск).
Примечания
Литература
Ссылки
www.gpedia.com