Чемпионы и призёры Олимпиады в Токио 1964. Олимпийские игры 1964
Токио 1964 | Олимпийские игры
Игры ХVIII Олимпиады
10 - 24 октября 1964 года в Токио, Япония прошли Игры ХVIII Олимпиады. Впервые Игры проводились на азиатском континенте. На этот раз число участников сократилось до 5140, но увеличилось количество стран - 93.
В программу Игр впервые включили волейбол и дзюдо. Было установлено 35 мировых рекордов и обновлено 77 олимпийских.
Сборная СССР завоевала наибольшее число медалей, но уступила сборной США по количеству золотых наград (30 - у Советского Союза и 36 - у американской сборной).
Команду СССР, выступившую на Играх составили 319 спортсменов: 256 мужчин и 63 женщины. Удачно выступили на Играх Олимпиады советские боксеры, гимнасты, борцы, волейболисты, штангисты, фехтовальщики и пятиборцы.
Впервые в истории нашей сборной было завоёвано золото в плавании. Первую золотую медаль принесла Галина Прозуменщикова на дистанции 200 м брассом с новым олимпийским рекордом.
Лучшим боксером турнира признали советского спортсмена Валерия Попенченко - он был удостоен специального приза для боксеров-любителей кубка Вэла Баркера.
Пятикратной олимпийской чемпионкой стала гимнастка Полина Астахова.
Два золота выиграла выдающаяся легкоатлетка Тамара Пресс.
Вячеслав Иванов в академической гребле стал трехкратным олимпийским чемпионом (он выигрывал золотые медали в 1956 и 1960 гг.).
Мужская сборная СССР по волейболу стала первым в истории олимпийским чемпионом,
Доказал свое звание лучшего спортсмена мира Валерий Брумель, победитель в прыжках в высоту.
Вторую золотую медаль в марафонском беге завоевал стайер из Эфиопии Абебе Бекила. 4 золотые медали выиграл в плавании американец Дон Шоландер, ставший самым знаменитым из участников Олимпиады.
| СССР | 30 | 31 | 35 | 96 | |
| США | 36 | 26 | 28 | 90 | |
| Объединённая германская команда | 10 | 22 | 18 | 50 | |
| Япония | 16 | 5 | 8 | 29 | |
| Италия | 10 | 10 | 7 | 27 |
www.infosport.ru
Зимние Олимпийские игры 1964 - WikiVisually
1. Инсбрук – Innsbruck is the capital city of Tyrol in western Austria. It is located in the Inn valley, at its junction with the Wipp valley, Innsbruck lies about halfway between Munich in Germany and Verona in Italy. Located in the valley between high mountains, the so-called North Chain in the Karwendel Alps to the north. Innsbruck is an internationally renowned winter sports centre, and hosted the 1964 and 1976 Winter Olympics as well as the 1984 and 1988 Winter Paralympics, Innsbruck also hosted the first Winter Youth Olympics in 2012. The name translates as Inn bridge, earliest traces suggest initial inhabitation in the early Stone Age. Surviving pre-Roman place names show that the area has been populated continuously, in the 4th century the Romans established the army station Veldidena at Oenipons, to protect the economically important commercial road from Verona-Brenner-Augsburg in their province of Raetia. The first mention of Innsbruck dates back to the name Oeni Pontum or Oeni Pons which is Latin for bridge over the Inn, the Counts of Andechs acquired the town in 1180. In 1248 the town passed into the hands of the Counts of Tyrol, the citys arms show a birds-eye view of the Inn bridge, a design used since 1267. The route over the Brenner Pass was then a major transport, the revenues generated by serving as a transit station enabled the city to flourish. Innsbruck became the capital of all Tyrol in 1429 and in the 15th century the city became a centre of European politics, the city benefited from the emperors presence as can be seen for example in the Hofkirche. Here a funeral monument for Maximilian was planned and erected partly by his successors, the ensemble with a cenotaph and the bronze statues of real and mythical ancestors of the Habsburgian emperor are one of the main artistic monuments of Innsbruck. A regular postal service between Innsbruck and Mechelen was established in 1490 by the Thurn-und-Taxis-Post, in 1564 Ferdinand II, Archduke of Austria received the rulership over Tirol and other Further Austrian possessions administrated from Innsbruck up to the 18th century. He had Schloss Ambras built and arranged there his unique Renaissance collections nowadays mainly part of Viennas Kunsthistorisches Museum, up to 1665 a stirps of the Habsburgian dynasty ruled in Innsbruck with an independent court. In the 1620s the first opera house north of the Alps was erected in Innsbruck, in 1669 the university was founded. Also as a compensation for the court as Emperor Leopold I again reigned from Vienna, during the Napoleonic Wars Tyrol was ceded to Bavaria, ally of France. Andreas Hofer led a Tyrolean peasant army to victory in the Battles of Bergisel against the combined Bavarian and French forces, the combined army later overran the Tyrolean militia army and until 1814 Innsbruck was part of Bavaria. After the Vienna Congress Austrian rule was restored, until 1918, the town was part of the Austrian monarchy, head of the district of the same name, one of the 21 Bezirkshauptmannschaften in the Tyrol province. The Tyrolean hero Andreas Hofer was executed in Mantua, his remains were returned to Innsbruck in 1823, during World War I, the only recorded action taking place in Innsbruck was near the end of the war
2. Австрия – Austria, officially the Republic of Austria, is a federal republic and a landlocked country of over 8.7 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Hungary and Slovakia to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, the territory of Austria covers 83,879 km2. The terrain is mountainous, lying within the Alps, only 32% of the country is below 500 m. The majority of the population speaks local Bavarian dialects of German as their native language, other local official languages are Hungarian, Burgenland Croatian, and Slovene. The origins of modern-day Austria date back to the time of the Habsburg dynasty, from the time of the Reformation, many northern German princes, resenting the authority of the Emperor, used Protestantism as a flag of rebellion. Following Napoleons defeat, Prussia emerged as Austrias chief competitor for rule of a greater Germany, Austrias defeat by Prussia at the Battle of Königgrätz, during the Austro-Prussian War of 1866, cleared the way for Prussia to assert control over the rest of Germany. In 1867, the empire was reformed into Austria-Hungary, Austria was thus the first to go to war in the July Crisis, which would ultimately escalate into World War I. The First Austrian Republic was established in 1919, in 1938 Nazi Germany annexed Austria in the Anschluss. This lasted until the end of World War II in 1945, after which Germany was occupied by the Allies, in 1955, the Austrian State Treaty re-established Austria as a sovereign state, ending the occupation. In the same year, the Austrian Parliament created the Declaration of Neutrality which declared that the Second Austrian Republic would become permanently neutral, today, Austria is a parliamentary representative democracy comprising nine federal states. The capital and largest city, with a population exceeding 1.7 million, is Vienna, other major urban areas of Austria include Graz, Linz, Salzburg and Innsbruck. Austria is one of the richest countries in the world, with a nominal per capita GDP of $43,724, the country has developed a high standard of living and in 2014 was ranked 21st in the world for its Human Development Index. Austria has been a member of the United Nations since 1955, joined the European Union in 1995, Austria also signed the Schengen Agreement in 1995, and adopted the euro currency in 1999. The German name for Austria, Österreich, meant eastern realm in Old High German, and is cognate with the word Ostarrîchi and this word is probably a translation of Medieval Latin Marchia orientalis into a local dialect. Austria was a prefecture of Bavaria created in 976, the word Austria is a Latinisation of the German name and was first recorded in the 12th century. Accordingly, Norig would essentially mean the same as Ostarrîchi and Österreich, the Celtic name was eventually Latinised to Noricum after the Romans conquered the area that encloses most of modern-day Austria, around 15 BC. Noricum later became a Roman province in the mid-first century AD, heers hypothesis is not accepted by linguists. Settled in ancient times, the Central European land that is now Austria was occupied in pre-Roman times by various Celtic tribes, the Celtic kingdom of Noricum was later claimed by the Roman Empire and made a province
3. Олимпийский огонь – The Olympic flame is a symbol of the Olympic Games. Commemorating the theft of fire from the Greek god Zeus by Prometheus, its origins lie in ancient Greece, the fire was introduced at the Games of the IX Olympiad 1928 in Amsterdam and it has been part of the modern Olympic Games ever since. The first fire of the Olympic Winter Games was introduced at the IV Olympic Winter Games 1936 in Garmisch-Partenkirchen, the Olympic Torch today is ignited several months before the opening ceremony of the Olympic Games at the site of the ancient Olympics in Olympia, Greece. Eleven women, representing the Vestal Virgins, perform a celebration at the Temple of Hera in which the torch is kindled by the light of the Sun, its rays concentrated by a parabolic mirror. The torch briefly travels around Greece via short relay, and then starts its transfer to the host city after a ceremony in the Panathenaic Stadium in Athens, the Olympic Torch Relay ends on the day of the opening ceremony in the central stadium of the Games. The final carrier is often kept unannounced until the last moment, the final bearer of the torch runs towards the cauldron, often placed at the top of a grand staircase, and then uses the torch to start the flame in the arena. It is considered to be an honor to be asked to light the Olympic flame. After being lit, the continues to burn throughout the Games, until the day of the closing ceremony and celebration. In the time of the games within the boundaries of Olympia. For the ancient Greeks, fire had divine connotations—it was thought to have stolen from the gods by Prometheus. Therefore, fire was present at many of the sanctuaries in Olympia. During the Olympic Games, which honoured Zeus, additional fires were lit at his temple, the modern Olympic flame is ignited at the site where the temple of Hera used to stand. The tradition was reintroduced during the 1928 Games, an employee of the Electric Utility of Amsterdam lit the first Olympic flame in the Marathon Tower of the Olympic Stadium in Amsterdam. The modern convention of moving the Olympic flame via a system from Greece to the Olympic venue began in 1936 in Germany. Carl Diem devised the idea of the relay for the 1936 Summer Olympics in Berlin that was organized by the Nazis under the guidance of Joseph Goebbels. The Krupp armaments company produced the torches in wood and metal, the Olympic flame was lit by a concave mirror in Olympia, Greece and transported over 3,187 kilometres by 3,331 runners in twelve days and eleven nights from Greece to Berlin. Leni Riefenstahl later staged the torch relay for the 1938 film Olympia, adolf Hitler saw the link with the ancient Games as the perfect way to illustrate his belief that classical Greece was an Aryan forerunner of the modern German Reich. There were minor protests in Yugoslavia and Czechoslovakia on the way, although most of the time the torch with the Olympic flame is still carried by runners, it has been transported in many different ways
4. Бобслей – Bobsleigh or bobsled is a winter sport in which teams of two or four teammates make timed runs down narrow, twisting, banked, iced tracks in a gravity-powered sled. The timed runs are combined to calculate the final score, all three types were adapted from boys delivery sleds and toboggans. Competition naturally followed, and to protect the class and rich visitors in the streets and byways of St Moritz. It has hosted the sport during two Olympics and is still in use today, International bobsleigh competitions are governed by the International Bobsleigh and Skeleton Federation, also known as FIBT from the French Fédération Internationale de Bobsleigh et de Tobogganing. National competitions are governed by bodies such as the United States Bobsled and Skeleton Federation. Although sledding on snow or ice had been popular in northern countries. It developed from two crestas attached together with a board and with a steering mechanism attached to the front cresta, the name of the sport appeared when competitors adopted the technique of bobbing back and forth inside the sled to increase its speed. This had both short- and long-term outcomes, in the term the guests began to scheme about and invent steering means for the sleds, which became the luge, bobsleighs. Long term, after a couple of years of happy pedestrian peril. Still in operation as of 2014, this has served as a host track during two Winter Olympics, as one of the few natural weather tracks in the world, it does not use artificial refrigeration. The first informal races took place on snow-covered roads, formal competitions started in 1884 at St. Moritz. Its not known how much the original track evolved in the years as the three sports matured and stabilized. The first club formed in 1897, and the first purpose-built track solely for bobsleds opened in 1902 outside of St Moritz, over the years, bobsleigh tracks evolved from straight runs to twisting and turning tracks. The original wooden sleds gave way to streamlined fiberglass and metal ones, the International Bobsleigh and Skeleton Federation was founded in 1923. Mens four-man bobsleigh appeared in the first ever Winter Olympic Games in 1924, though not included in the 1960 Winter Olympics, bobsleigh has featured in every Winter Olympics since. Womens bobsleigh competition began in the US in 1983 with two races in Lake Placid, New York, one held in February and the second held during the World Cup races in March 1983. Womens two-woman bobsleigh made its Olympic debut at the 2002 Winter Olympic Games, Bobsleigh is also contested at American, European, and World Cup championships. Germany and Switzerland have proven the most successful bobsleighing nations measured by overall success in European, World, World Cup, since the 1990s Germans have dominated in international competition, having won more medals than any other nation
5. Главные стадионы Олимпийских игр – Olympic Stadium is the name usually given to the main stadium of an Olympic Games. An Olympic stadium is the site of the opening and closing ceremonies, many, though not all, of these venues actually contain the words Olympic Stadium as part of their names. Olympic Stadium may also be named a stadium which hosts Olympic sports. In the case of the Summer Olympics, athletics competitions and the final are traditionally held in the Olympic Stadium. Exceptions to this have occurred though at the 1900,1996 and 2016 Summer Olympics as well as at the 2010 and 2018 Summer Youth Olympic Games, early Winter Games often used figure skating venues as focal points. These were often designated as the Olympic Stadium, usually hosting the opening and closing ceremonies, a number of stadiums have been used in more than one Olympics, in those cities that have held the Games more than once. Lysgårdsbakkene was the stadium of a Winter Olympics and a Winter Youth Olympic Games. Bergiselschanze was the stadium of two Winter Olympics and one Winter YOG. Olympiahalle jointly shared the Olympic Stadium role with Bergiselschanze during the two Winter Olympics, but not during the Winter YOG, only one stadium, the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum, has been the main stadium of two Summer Olympics. In addition to the inaugural Summer Olympics, Panathinaiko Stadio was also the stadium of the only Intercalated Games held. A number, including both the Panathinaiko Stadio and the Vélodrome de Vincennes, have hosted events at subsequent Olympics. The London Games of 2012 were not opened and closed at the rebuilt Wembley Stadium, the site of the 1948 Olympic Stadium, Wembley was, however, the venue for some 2012 Olympic football matches. Likewise, the Melbourne Cricket Ground, which was the stadium for the 1956 games. Lake Placids 1930 Olympic Stadium was utilized in the 1980 Lake Placid games as the speed skating venue, olympiahalle hosted figure skating and short-track speed skating during the 2012 Winter Youth Olympics. Stockholm Olympic Stadium hosted equestrian events for the 1956 Summer Olympics, Olympic Past & Future Stadiums - BALLPARKS. com Summer Olympic Stadiums 1896 - on Google Maps
6. Бергизель – The Bergisel Sprungschanze Stadion, which has a capacity of 26,000, is a ski jumping hill stadium located in Bergisel in Innsbruck, Austria. It is one of the more important venues in the FIS Ski Jumping World Cup and its first competitions were held in the 1920s using simple wood constructions. The larger hill was first built in 1930 and was rebuilt before the 1964 Winter Olympics for the large hill event. Twelve years later, the hosted the same event. The hill in its current form was finished in 2003 and was designed by the British Iraqi architect Zaha Hadid, list of ski jumping hills Stadium images 1964 Winter Olympics official report
7. Зимние Олимпийские игры 1960 – The 1960 Winter Olympics was a winter multi-sport event held between February 18–28,1960 in Squaw Valley, California, United States. Squaw Valley was chosen to host the Games at the 1956 meeting of the International Olympic Committee and it was an undeveloped resort in 1955, so from 1956 to 1960 the infrastructure and all of the venues were built at a cost of US$80,000,000. It was designed to be intimate, allowing spectators and competitors to walk to all the venues. Squaw Valley hosted athletes from thirty nations who competed in four sports, womens speed skating and biathlon made their Olympic debuts. The organizers decided the bobsled events did not warrant the cost to build a venue, so for the first, the Soviet Union dominated the medal count winning twenty-one medals, seven of which were gold. Soviet speed skaters Yevgeny Grishin and Lidiya Skoblikova won two medals each. Swedish cross-country skier Sixten Jernberg added a gold and silver to the four medals he won at the 1956 Winter Games, cold War politics forced the IOC to debate the participation of China, Taiwan, North Korea and East Germany. In 1957 the United States government threatened to deny visas to athletes from Communist countries, the IOC responded with a threat to revoke Squaw Valleys right to host the 1960 Games. The United States conceded and allowed entry to athletes from Communist countries, Squaw Valley was a struggling ski resort with minimal facilities, which made its selection to host the 1960 Winter Olympics a surprise. Wayne Poulsen and Alexander Cushing, who were inspired to an Olympic bid by an article mentioning that Reno, Nevada. Poulsen, president of the Squaw Valley Development Company, petitioned California Governor Goodwin Knight to support a bid to host the Olympic Games, knights administration agreed and recommended that the California Legislature appropriate $1,000,000 to the effort. Based on the support received from the State of California. Preliminary reports were drafted and submitted to the IOC, which was considering bids from Innsbruck, Austria, St. Moritz, Switzerland and Chamonix, another $4,000,000 were committed by the State Legislature, which met Brundages requirements. On April 4,1956, the right to host the 1960 Winter Olympics was officially awarded to Squaw Valley, Squaw Valley in 1956 consisted of one chair lift, two rope tows, and a fifty-room lodge. Cushing presented the site as a canvas of unspoiled environment. The obscurity of the location was underscored at the ceremonies of the 1956 Winter Olympics. Traditionally the mayor of the current host city passes a flag to the mayor of the next host city signalling the transfer of the Games, since Squaw Valley was an unincorporated village it had no city government. John Garland, an IOC member from California, was asked to stand in, after winning the right to host the Games, the California Olympic Commission was formed
8. Зимние Олимпийские игры 1968 – The 1968 Winter Olympics, officially known as the X Olympic Winter Games, were a winter multi-sport event which was celebrated in 1968 in Grenoble, France and opened on 6 February. Norway won the most medals, the first time a country other than the USSR had done so since the USSR first entered the Winter Games in 1956, frenchman Jean-Claude Killy won three gold medals in all the alpine skiing events. In womens figure skating, Peggy Fleming won the only United States gold medal, the year 1968 marked the first time the IOC first permitted East and West Germany to enter separately, and the first time the IOC ever ordered drug and gender testing of competitors. The application was given to the IOC during a meeting between IOC executives and representatives of international sport agencies in Lausanne in February 1963. Between 1946 and 1962 the number of inhabitants in Grenoble increased from 102,000 to 159,000, the development of the infrastructure could not keep up with this rapid increase and was for the most part at the same level as before the Second World War. The 61st IOC session, where the awarding of the Olympic Games should have been voted for and this session was moved to Baden-Baden because Kenya refused entry to IOC members from Portugal and South Africa for political reasons. Due to a lack of time only the Summer Games of 1968 could be voted for, the vote finally took place in Innsbruck on 28 January 1964, one day before the start of the 1964 Winter Olympic Games. After Grenoble was voted as the host city the French National Olympic Sports Committee decided the foundation of the organisation committee. The Comité d’Organisation des dixièmes Jeux Olympiques, the committee for the organisation of the 10th Olympic Games, albert Michallon, alongside being the former mayor of Grenoble, was also president of COJO. The upper panel was made up of the assembly with its 340 members and the supervisory board conduct business with 39 members,19 of which were appointed. The general secretary consisted of five departments and 17 subordinate departments. The number of employees grew to 1920 in February 1968, minister for Youth and Sport Francois Missoffe formed an interministerial committee for the coordination of the work commissioned by prime minister Georges Pompidou. Just over 7000 soldiers of the French armed forces and also employees of the ministries for Youth and Sport, Finance, Social Building, Education, Post, Culture, the sum of the investments contributed to 1.1 billion Francs. The government contributed 47. 08%, the Isere Department 3. 65%, the city of Grenoble 20. 07% and the surrounding communities 1. 37%. Different institutions, such as the train company SNCF, the television broadcaster ORTF, the government housing association, to test the new sport complex and to improve organisational processes they organized International Sports Weeks. From 20 January to 19 February 1967 speed skating competitions and ski races took place, from 12 to 15 October 1967 an ice hockey tournament, on 16 December 1967, the olympic torch was lit in ancient Olympia in Greece. The route of the relay at first led over Mount Olympus to Athens. From there, the torch was flown by an Air France Boeing 707 to the Paris-Orly airport
9. Калгари – Calgary is a city in the Canadian province of Alberta. It is situated at the confluence of the Bow River and the Elbow River in the south of the province, in an area of foothills and prairie, the city anchors the south end of what Statistics Canada defines as the Calgary–Edmonton Corridor. The city had a population of 1,239,220 in 2016, making it Albertas largest city, also in 2016, Calgary had a metropolitan population of 1,392,609, making it the fourth-largest census metropolitan area in Canada. The Calgary CMA is home to the second-highest number of head offices in Canada among the countrys 800 largest corporations. In 1988, Calgary became the first Canadian city to host the Winter Olympic Games, Calgary was named after Calgary on the Isle of Mull, Scotland. In turn, the name originates from a compound of kald and gart, similar Old Norse words, meaning cold and garden, alternatively, the name might be Gaelic Cala ghearraidh, meaning beach of the meadow, or Gaelic for either clear running water or bay farm. The Calgary area was inhabited by people whose presence has been traced back at least 11,000 years. Before the arrival of Europeans, the area was inhabited by the Blackfoot, Blood, Peigan, in 1787, cartographer David Thompson spent the winter with a band of Peigan encamped along the Bow River. He was a Hudsons Bay Company trader and the first recorded European to visit the area, John Glenn was the first documented European settler in the Calgary area, in 1873. The site became a post of the North-West Mounted Police, the NWMP detachment was assigned in 1875 to protect the western plains from US whisky traders, and to protect the fur trade. Originally named Fort Brisebois, after NWMP officer Éphrem-A, Brisebois, it was renamed Fort Calgary in 1876 by Colonel James Macleod. When the Canadian Pacific Railway reached the area in 1883, over a century later, the Canadian Pacific Railway headquarters moved to Calgary from Montreal in 1996. Calgary was officially incorporated as a town in 1884, and elected its first mayor, in 1894, it was incorporated as The City of Calgary in what was then the North-West Territories. The Calgary Police Service was established in 1885 and assumed municipal, local duties from the NWMP, the Calgary Fire of 1886 occurred on November 7,1886. Fourteen buildings were destroyed with losses estimated at $103,200, although no one was killed or injured, city officials drafted a law requiring all large downtown buildings to be built with Paskapoo sandstone, to prevent this from happening again. After the arrival of the railway, the Dominion Government started leasing grazing land at minimal cost, as a result of this policy, large ranching operations were established in the outlying country near Calgary. Already a transportation and distribution hub, Calgary quickly became the centre of Canadas cattle marketing and meatpacking industries. By the late 19th century, the Hudsons Bay Company expanded into the interior and established posts along rivers that later developed into the cities of Winnipeg, Calgary
10. Канада – Canada is a country in the northern half of North America. Canadas border with the United States is the worlds longest binational land border, the majority of the country has a cold or severely cold winter climate, but southerly areas are warm in summer. Canada is sparsely populated, the majority of its territory being dominated by forest and tundra. It is highly urbanized with 82 per cent of the 35.15 million people concentrated in large and medium-sized cities, One third of the population lives in the three largest cities, Toronto, Montreal and Vancouver. Its capital is Ottawa, and other urban areas include Calgary, Edmonton, Quebec City, Winnipeg. Various aboriginal peoples had inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years prior to European colonization. Pursuant to the British North America Act, on July 1,1867, the colonies of Canada, New Brunswick and this began an accretion of provinces and territories to the mostly self-governing Dominion to the present ten provinces and three territories forming modern Canada. With the Constitution Act 1982, Canada took over authority, removing the last remaining ties of legal dependence on the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Canada is a parliamentary democracy and a constitutional monarchy, with Queen Elizabeth II being the head of state. The country is officially bilingual at the federal level and it is one of the worlds most ethnically diverse and multicultural nations, the product of large-scale immigration from many other countries. Its advanced economy is the eleventh largest in the world, relying chiefly upon its abundant natural resources, Canadas long and complex relationship with the United States has had a significant impact on its economy and culture. Canada is a country and has the tenth highest nominal per capita income globally as well as the ninth highest ranking in the Human Development Index. It ranks among the highest in international measurements of government transparency, civil liberties, quality of life, economic freedom, Canada is an influential nation in the world, primarily due to its inclusive values, years of prosperity and stability, stable economy, and efficient military. While a variety of theories have been postulated for the origins of Canada. In 1535, indigenous inhabitants of the present-day Quebec City region used the word to direct French explorer Jacques Cartier to the village of Stadacona, from the 16th to the early 18th century Canada referred to the part of New France that lay along the St. Lawrence River. In 1791, the area became two British colonies called Upper Canada and Lower Canada collectively named The Canadas, until their union as the British Province of Canada in 1841. Upon Confederation in 1867, Canada was adopted as the name for the new country at the London Conference. The transition away from the use of Dominion was formally reflected in 1982 with the passage of the Canada Act, later that year, the name of national holiday was changed from Dominion Day to Canada Day
wikivisually.com
Зимние Олимпийские игры 1964 Википедия
| IX Зимние Олимпийские Игры | |
| Эмблема Зимних Олимпийских игр 1964 | |
| Инсбрук, Австрия | |
| 36 | |
| 1091 (892 мужчин, 199 женщин) | |
| 34 комплекта в 10 видах спорта | |
| 29 января 1964 | |
| Адольф Шерф | |
| 9 февраля 1964 | |
| Йозеф Ридер (Josef Rieder) | |
| Пол Асте (Paul Aste)(бобслей) | |
| Бергизель (Bergisel) | |
| 19601968 | |
| Официальный сайт | |
| Зимние Олимпийские игры 1964 на Викискладе | |
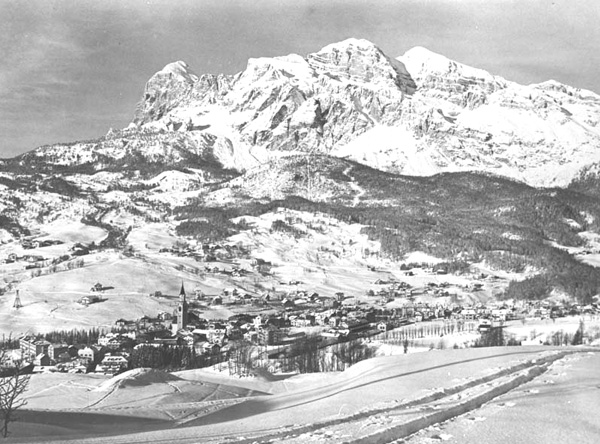
IX зимние Олимпийские игры проводились в Инсбруке.
Содержание
- 1 Выбор города
- 2 Виды спорта
- 3 Страны-участницы
- 4 Расписание соревнований
- 5 Медальный зачёт
- 6 Призёры игр
- 7 Литература
- 8 Ссылки
Выбор города[ | код]
Соперником австрийского города Инсбрук были: Калгари (Канада) и Лахти (Финляндия). В 1959 году МОК на своей сессии в Мюнхене предоставил право проведения игр столице Тироля.
| Город | Страна | Раунд 1 |
| Инсбрук | Австрия | 48 |
| Калгари | Канада | 12 |
| Лахти | Финляндия | 1 |
Виды спорта[ | код]
Впервые на Зимних Олимпийских играх появился санный спорт. Также в программу были возвращены соревнования по бобслею.
Основные виды.
|
ru-wiki.ru
Зимние Олимпийские игры 1964 - Gpedia, Your Encyclopedia
Текущая версия страницы пока не проверялась опытными участниками и может значительно отличаться от версии, проверенной 29 мая 2017; проверки требуют 25 правок.
 Текущая версия страницы пока не проверялась опытными участниками и может значительно отличаться от версии, проверенной 29 мая 2017; проверки требуют 25 правок.
Текущая версия страницы пока не проверялась опытными участниками и может значительно отличаться от версии, проверенной 29 мая 2017; проверки требуют 25 правок. IX зимние Олимпийские игры проводились в Инсбруке.
Выбор города
Соперником австрийского города Инсбрук были: Калгари (Канада) и Лахти (Финляндия). В 1959 году МОК на своей сессии в Мюнхене предоставил право проведения игр столице Тироля.
Виды спорта
Впервые на Зимних Олимпийских играх появился санный спорт. Также в программу были возвращены соревнования по бобслею.
Основные виды.
В скобках количество разыгрываемых комплектов медалей.
Страны-участницы
Участвовало 36 стран. Это явилось рекордом для зимних игр. Команды ГДР и ФРГ выступали объединённой командой. Дебютировали на Зимних Олимпийских играх Индия, КНДР и Монголия
Расписание соревнований
| ● | Церемония открытия | ● | Квалификация соревнований | ● | Финалы соревнований | ● | Показательные выступления | ● | Церемония закрытия |
* Для более полного ознакомления с результатами отдельных видов спорта на данной олимпиаде нажмите на названия конкретного вида спорта в данной таблице.
Медальный зачёт
 Победы советских спортсменов на IX Зимних Олимпийских играх (Инсбрук, Австрия). Марка СССР, 1964.
Победы советских спортсменов на IX Зимних Олимпийских играх (Инсбрук, Австрия). Марка СССР, 1964. Жирным шрифтом выделено самое большое количество медалей в своей категории
Призёры игр
Литература
- Год Олимпийский. Инсбрук, 1964. Девятые зимние олимпийские игры. Токио, 1964. Восемнадцатые летние олимпийские игры. [Альбом] / Сост. В. В. Денисов. — М.: Физкультура и спорт, 1965. — 483 с.
- Над Инсбруком звучат фанфары. [Сборник] / Сост. В. Г. Ушаков. — М.: Физкультура и спорт, 1964. — 288 с.
Ссылки
www.gpedia.com
 |
Лариса Латынина, Полина Астахова, Елена Волчецкая, Тамара Замотайлова, Тамара Манина, Людмила Громова Командное первенство |
 |
Полина Астахова Брусья |
 |
Борис Шахлин Перекладина |
 |
Лариса Латынина Вольные упражнения |
 |
Виктор Лисицкий Абсолютное первенство |
 |
Борис Шахлин Абсолютное первенство |
 |
Борис Шахлин, Виктор Лисицкий, Виктор Леонтьев, Юрий Цапенко, Юрий Титов, Сергей Диомидов Командное первенство |
 |
Лариса Латынина Абсолютное первенство |
 |
Виктор Лисицкий Вольные упражнения |
 |
Лариса Латынина Опорный прыжок |
 |
Виктор Лисицкий Опорный прыжок |
 |
Юрий Титов Перекладина |
 |
Полина Астахова Вольные упражнения |
 |
Тамара Манина Бревно |
 |
Полина Астахова Абсолютное первенство |
 |
Борис Шахлин Кольца |
 |
Юрий Цапенко Конь |
 |
Лариса Латынина Брусья |
 |
Лариса Латынина Бревно |
www.olympic-champions.ru
Девятые Зимние Олимпийские игры – OLYMPS.RU
Инсбрук, Австрия
Время проведения: с 29 января по 9 февраля 1964 года.
Представленные виды спортаБиатлонБобслейГорнолыжный спортКонькобежный спортЛыжное двоеборьеЛыжные гонкиПрыжки с трамплинаСанный спортФигурное катаниеХоккей
 Инсбрук прекрасно подготовился к Зимним Олимпийским играм 1964 года. Были сооружены новые и реконструированы имевшиеся спортивные сооружения. Однако оттепель резко осложнила обстановку соревнований. Специальным службам пришлось переместить 15000 кубометров снега из ложбин на санные, бобслейные и горнолыжные трассы.
Инсбрук прекрасно подготовился к Зимним Олимпийским играм 1964 года. Были сооружены новые и реконструированы имевшиеся спортивные сооружения. Однако оттепель резко осложнила обстановку соревнований. Специальным службам пришлось переместить 15000 кубометров снега из ложбин на санные, бобслейные и горнолыжные трассы.
Даже из-за погодных катаклизмов, Олимпийские игры в Инсбруке были проведены на очень высоком уровне. Олимпиада оказалась рекордной как по количеству участников, так и по обширности программы. 1111 спортсменов, в том числе 197 женщин, представлявших 37 стран, 36 команд — ГДР и ФРГ были представлены объединенной командой, боролись за награды в 34 видах соревнований 7 видов спорта. Напряженная спортивная борьба приносила победы представителям различных стран.
 В горнолыжном спорте сильнее других были олимпийцы Австрии и Франции. В составе горнолыжной команды Франции выступали сестры Кристина и Мариель Гойчель. Кристина выиграла золотую медаль в слаломе, а Мариэль — серебряную. В гигантском слаломе сестры поменялись местами.
В горнолыжном спорте сильнее других были олимпийцы Австрии и Франции. В составе горнолыжной команды Франции выступали сестры Кристина и Мариель Гойчель. Кристина выиграла золотую медаль в слаломе, а Мариэль — серебряную. В гигантском слаломе сестры поменялись местами.
В лыжных гонках у мужчин, как обычно, преимущество имели представители северных стран. В лыжных гонках женщин все три золотые медали оказались у спортсменок СССР.
 В конькобежном спорте у мужчин в каждом из четырех видов соревнований побеждали представители различных стран. Однако подлинную сенсацию принесли соревнования по скоростному бегу на коньках среди женщин: 9 из 12 разыгранных медалей завоевали спортсменки СССР. Все 4 золотые медали стали достоянием выдающейся спортсменки СССР и мира Лидии Скобликовой. Она установила на Олимпийских играх в Инсбруке три олимпийских рекорда. Никому в мире не удавалось добиться такого результата. Мировая пресса восторженно приветствовала успех Скобликовой. Австрийская газета «Бильд», анализируя причины ее успеха отмечала: «В ней сочетается сила, техника и тонкая гармония в движениях, что само по себе является искусством, позволяющим добиться таких выдающихся достижений». Американский журнал «Спорт иллюстрайтед» назвал Скобликову «лучшей конькобежкой, которую знал мир».
В конькобежном спорте у мужчин в каждом из четырех видов соревнований побеждали представители различных стран. Однако подлинную сенсацию принесли соревнования по скоростному бегу на коньках среди женщин: 9 из 12 разыгранных медалей завоевали спортсменки СССР. Все 4 золотые медали стали достоянием выдающейся спортсменки СССР и мира Лидии Скобликовой. Она установила на Олимпийских играх в Инсбруке три олимпийских рекорда. Никому в мире не удавалось добиться такого результата. Мировая пресса восторженно приветствовала успех Скобликовой. Австрийская газета «Бильд», анализируя причины ее успеха отмечала: «В ней сочетается сила, техника и тонкая гармония в движениях, что само по себе является искусством, позволяющим добиться таких выдающихся достижений». Американский журнал «Спорт иллюстрайтед» назвал Скобликову «лучшей конькобежкой, которую знал мир».
 Также сенсацией закончились соревнования в парном катании на коньках у фигуристов. Никто не сомневался в победе немецких спортсменов Килиус и Боймлера. Они уверенно побеждали своих соперников на крупнейших международных турнирах. Но победу одержали Людмила Белоусова и Олег Протопопов, ставшие первыми из спортсменов СССР олимпийскими чемпионами в фигурном катании на коньках.
Также сенсацией закончились соревнования в парном катании на коньках у фигуристов. Никто не сомневался в победе немецких спортсменов Килиус и Боймлера. Они уверенно побеждали своих соперников на крупнейших международных турнирах. Но победу одержали Людмила Белоусова и Олег Протопопов, ставшие первыми из спортсменов СССР олимпийскими чемпионами в фигурном катании на коньках.
Несмотря на сильные возражения, обусловленные большой опасностью травматизма, санный спорт был включен в программу соревнований. Первые два места в составе объединенной немецкой команды заняли спортсмены ГДР, положив начало серии побед в этом виде спорта.
Уверенно выступила хоккейная команда СССР, сумевшая нанести поражение всем соперникам. В 8 встречах игроки сборной СССР забросили 73 шайбы и пропустили в свои ворота лишь 11.
Победу в общекомандном зачете завоевали спортсмены сборной команды СССР при 162 очках и 25 медалях — 11 золотых, 8 серебряных, 6 бронзовых. Второе место заняла успешно выступившая команда Норвегии набрав 89,5 очка и завоевав 15 медалей — 3 золотых, 6 серебряных, 6 бронзовых. Третьими были австрийские спортсмены получив 79 очков и 12 медалей — 4 золотых, 5 серебряных, 3 бронзовых.
www.olymps.ru
Олимпийские игры 1964 года - это... Что такое Олимпийские игры 1964 года?
Олимпийские игры 1964 годаXVIII Летние Олимпийские игры проводились в Токио.
Медаль XVIII Летних Олимпийских игр
Полина Астахова в третий раз подряд стала олимпийской чемпионкой в составе команды СССР
Итоговый зачёт медалей
1. Объединенная команда ГДР и ФРГ
См. также
Летние Олимпийские игры 1964
Академическая гребля | Баскетбол | Бейсбол¹ | Бокс | Борьба | Велоспорт | Водное поло | Волейбол | Гимнастика | Гребля на байдарках и каноэ | Дзюдо | Конный спорт | Лёгкая атлетика | Парусный спорт | Плавание | Прыжки в воду | Современное пятиборье | Стрельба | Тяжёлая атлетика | Фехтование | Футбол | Хоккей на траве¹ Показательные соревнования
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
- Олимпийская чемпионка
- Олимпиада в Турине
Смотреть что такое "Олимпийские игры 1964 года" в других словарях:
Летние Олимпийские игры 1964 года — … Википедия
Олимпийские игры 1908 года — Игры IV Олимпиады Город организатор Лондон, Великобритания Страны участницы 22 Количество атлетов 2008 (1971 мужчин, 37 женщин) Разыгрывается медалей 110 комплектов медалей в 22 видах спорта[a 1] Цере … Википедия
Олимпийские игры 2008 года — XXIX летние Олимпийские игры Город организатор Пекин, Китай Страны участницы 204 Количество атлетов 11 099 Разыгрывается медалей 302 комплекта наград в 28 видах спорта … Википедия
Олимпийские Игры 2014 года — XXII зимние Олимпийские игры Город организатор Сочи Страны участ … Википедия
Олимпийские игры 1912 года — V Летние Олимпийские Игры Город организатор Стокгольм, Швеция Страны участницы 28 Количество атлетов 2407 (48 женщин) Разыграно медалей 109 комплекта Церемония открытия 5 мая 1912 Церемония закрытия 27 июня 1912 Летние Олимпийские … Википедия
Летние Олимпийские игры 1964 — XVIII летние Олимпийские Игры Город организатор … Википедия
XXІX Олимпийские Игры 2008 года в Пекине — XXIX летние Олимпийские игры Город организатор Пекин, Китай Страны участницы 204 Количество атлетов 11 099 Разыгрывается медалей 302 комплекта наград в 28 видах спорта … Википедия
Зимние Олимпийские Игры 2014 года — XXII зимние Олимпийские игры Город организатор Сочи Страны участ … Википедия
Зимние Олимпийские игры 2006 года — XX зимние Олимпийские игры Город организатор Турин, Италия Страны участницы 80 Количество атлетов 2508 Разыгрывается медалей 84 комплекта в 7 видах спорта Церемония открытия 10 февраля … Википедия
Зимние Олимпийские игры 1924 года — I зимние Олимпийские Игры Город организатор Шамони, Франция Страны участницы 16 Количество атлетов 258 (247 мужчин, 11 женщин) Разыгрывается медалей 16 комплектов в 9 видах спорта … Википедия
dic.academic.ru